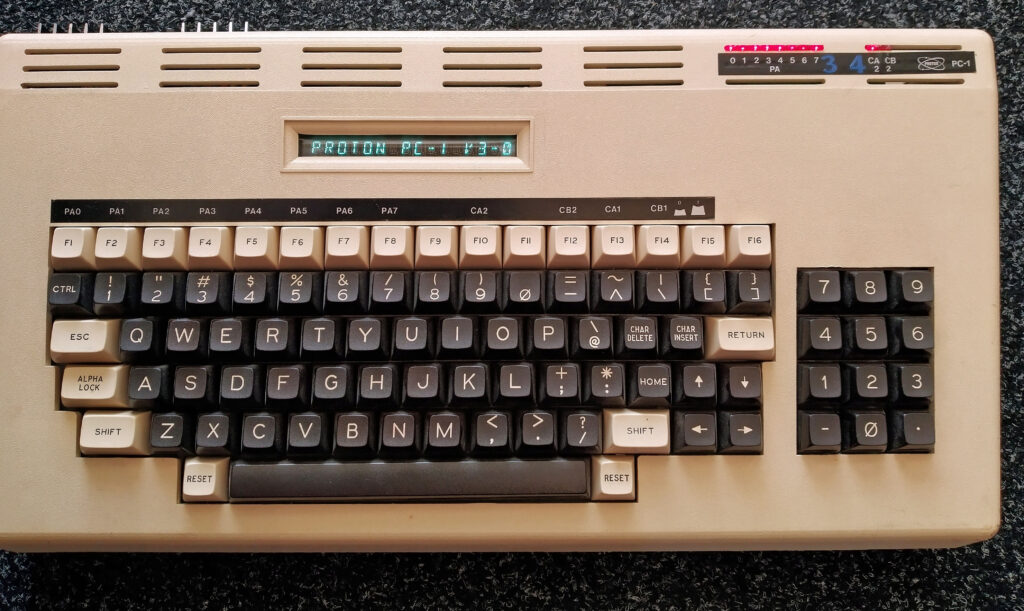
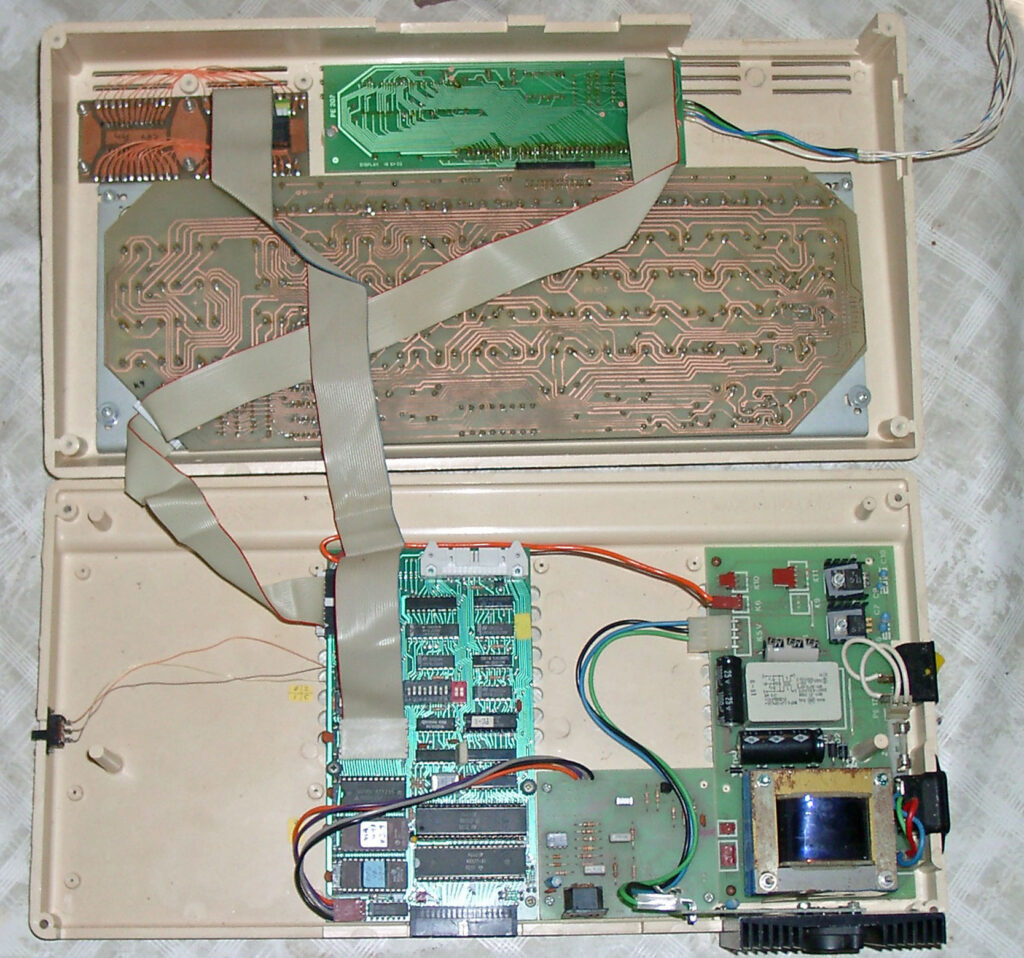
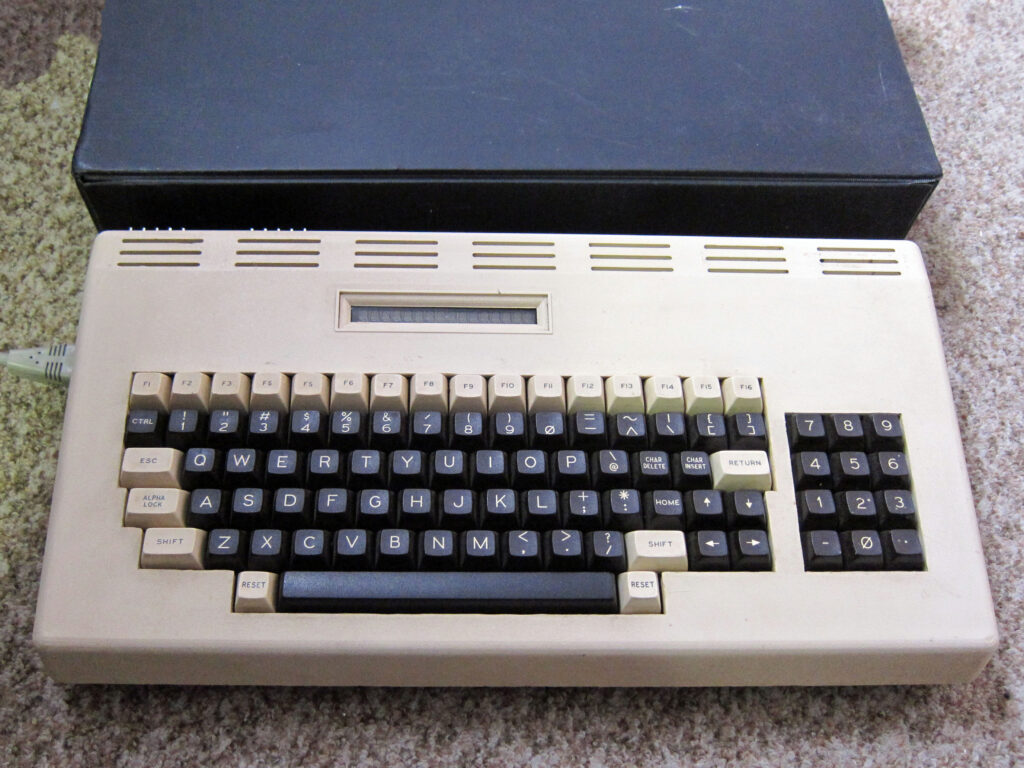
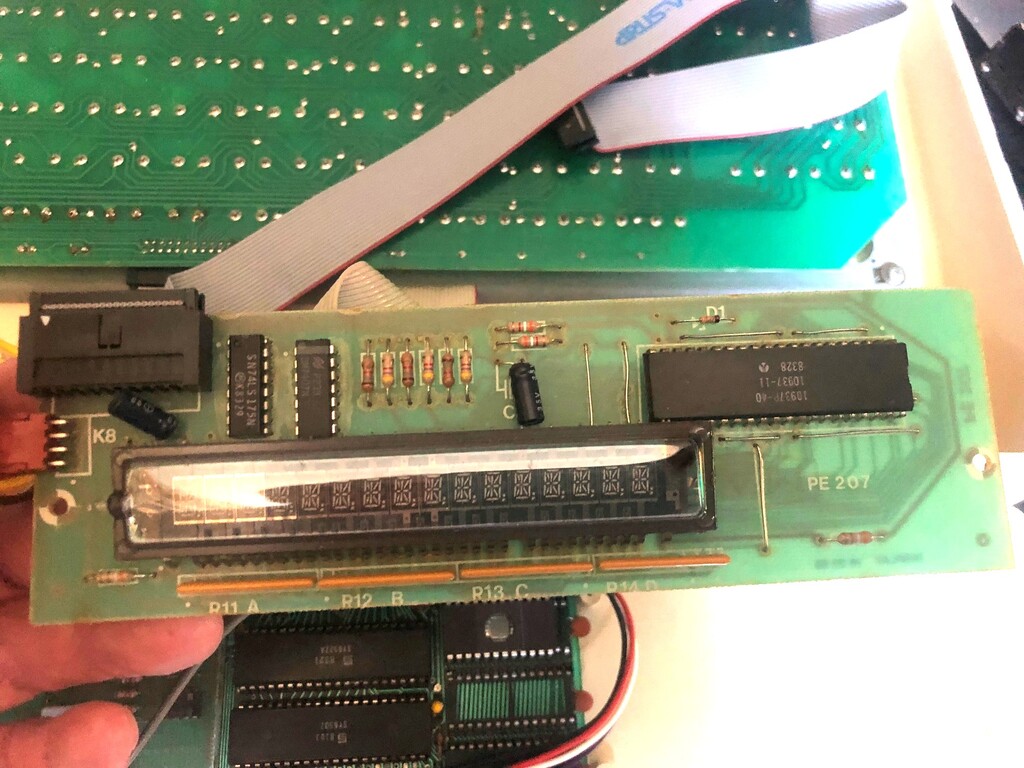
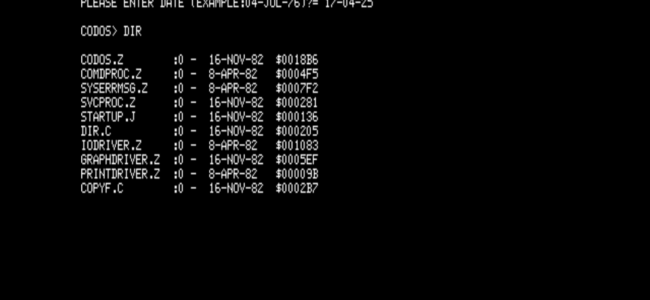
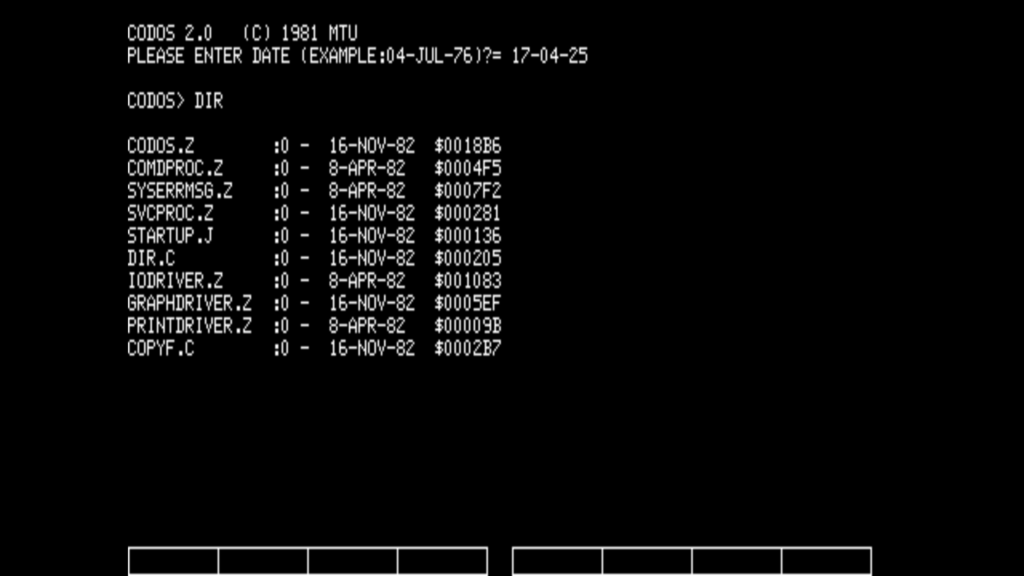
Scandinavian? KIM
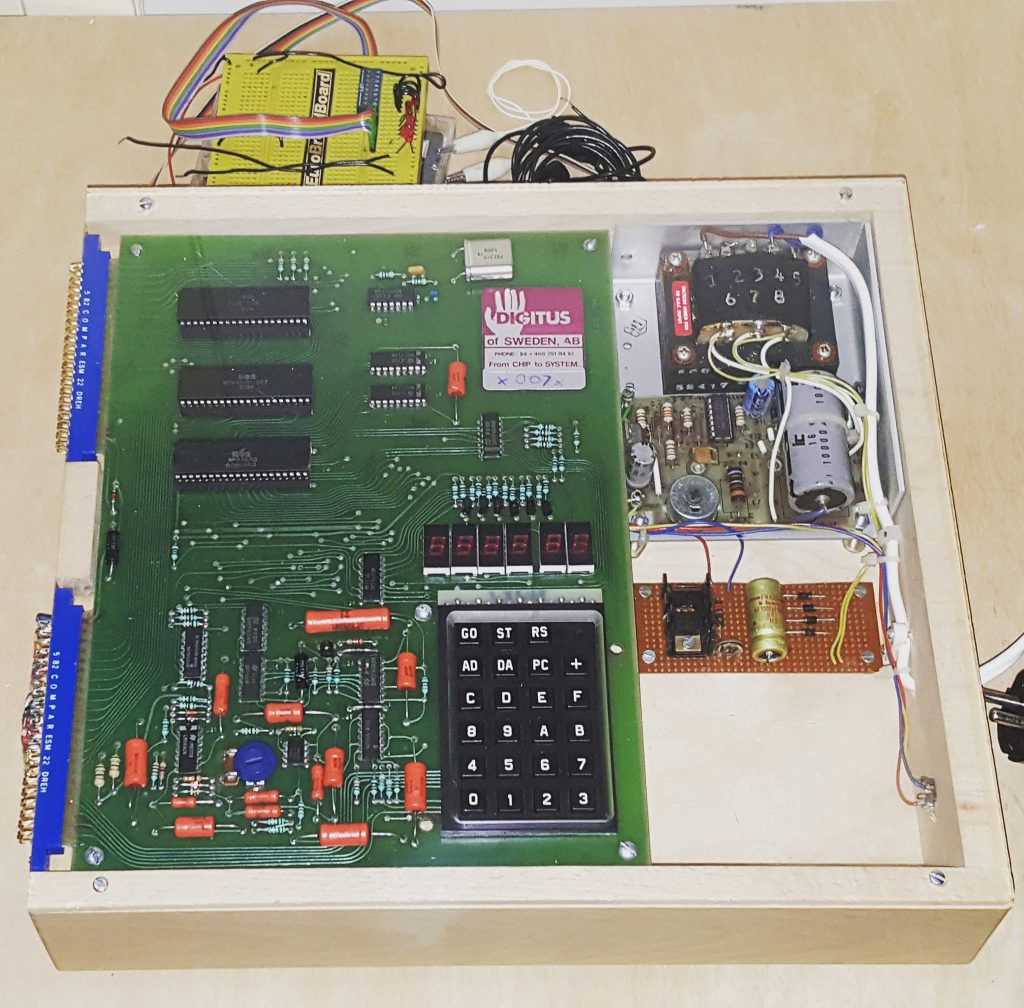

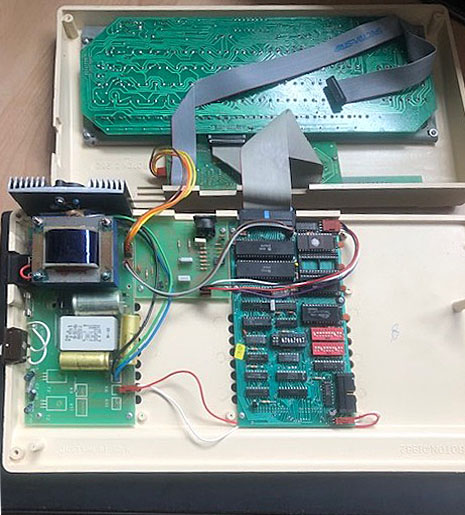
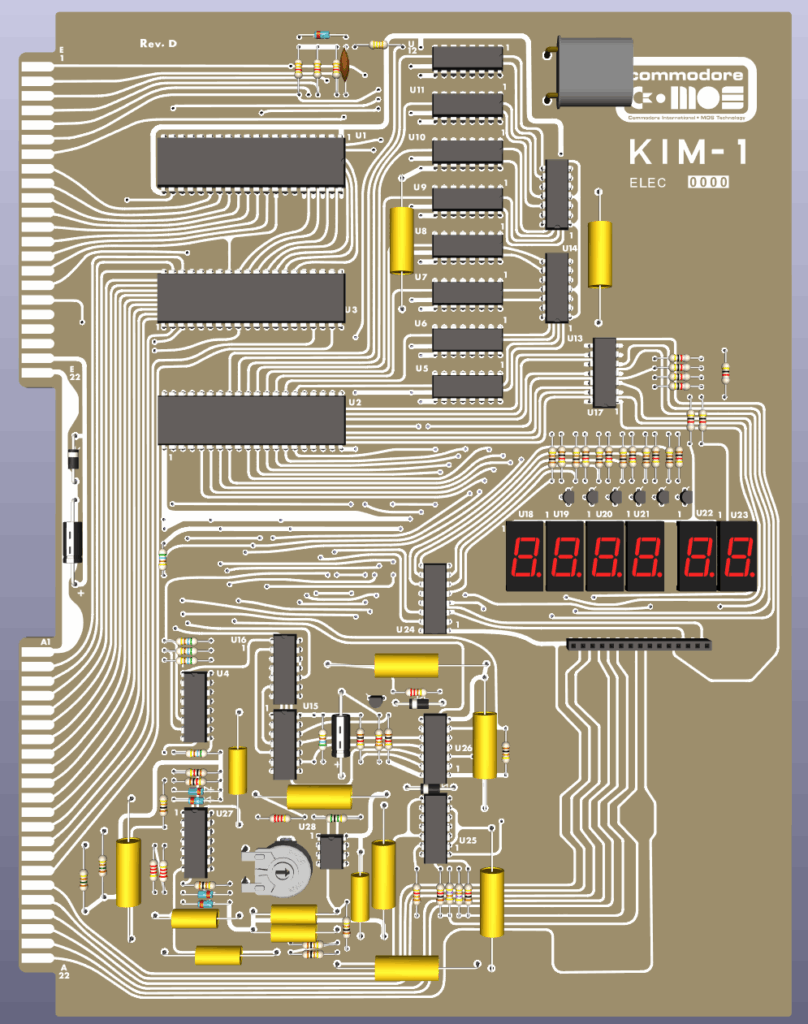
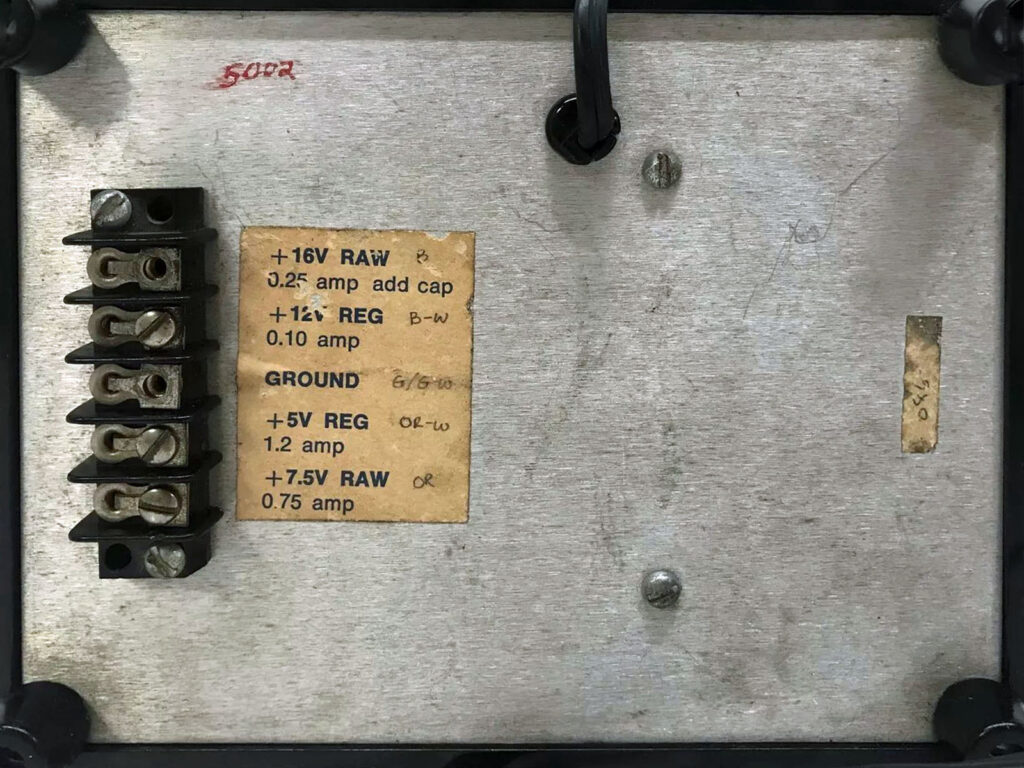
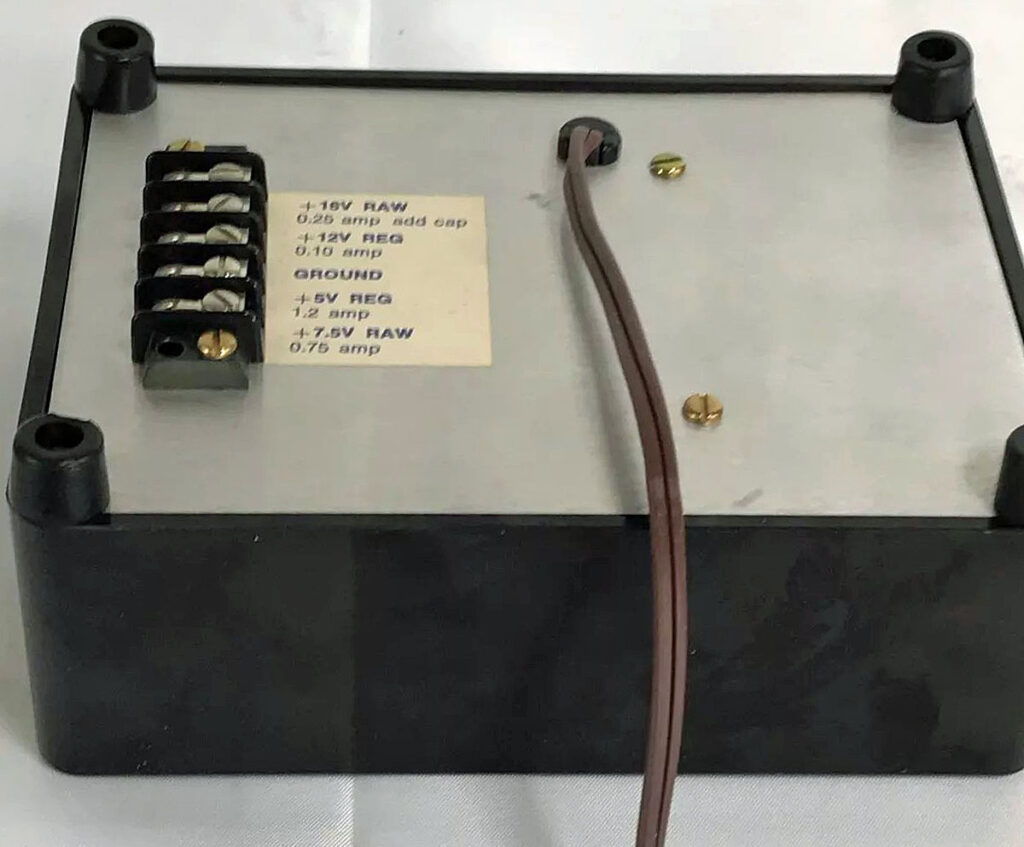
Found this photo in a Facebook group, from an Ebay auction. , no more information known. Looks like a standard KIM-1 with 2x 2114 SRAM ICs for the standard 1K RAM.
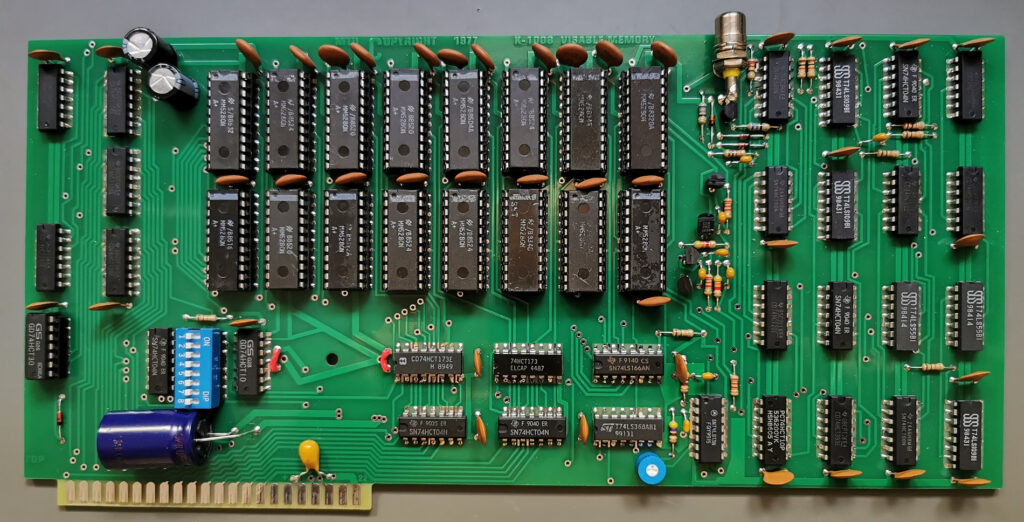
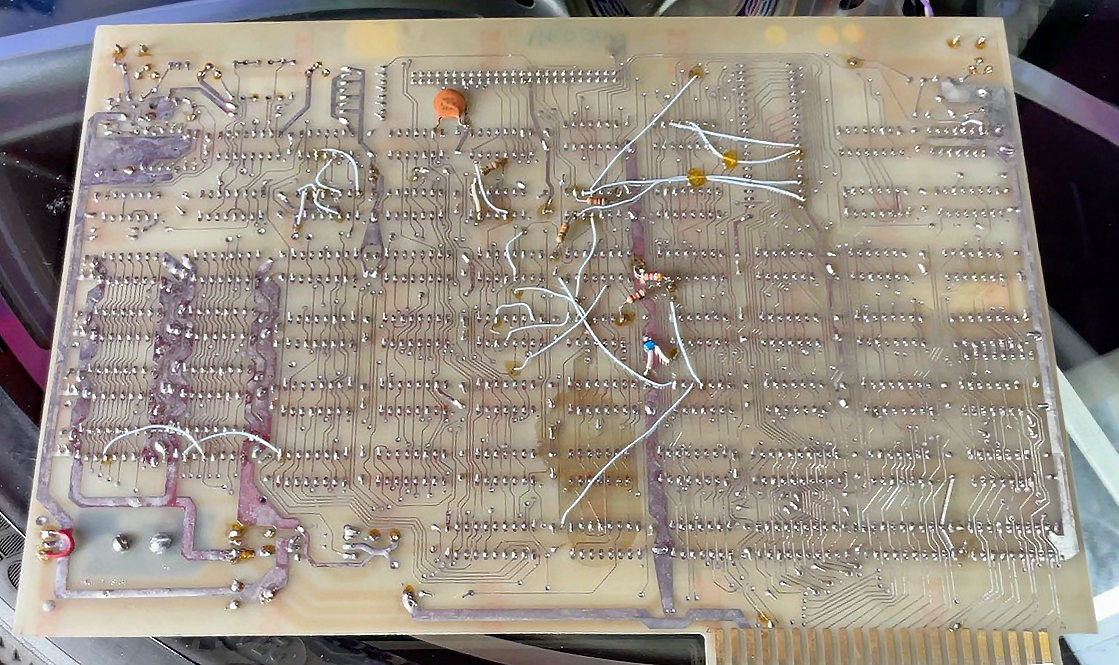
Recently on Ebay an identical KIM-1 lookalike showed up. The PCB is inspired but clearly newly designed.
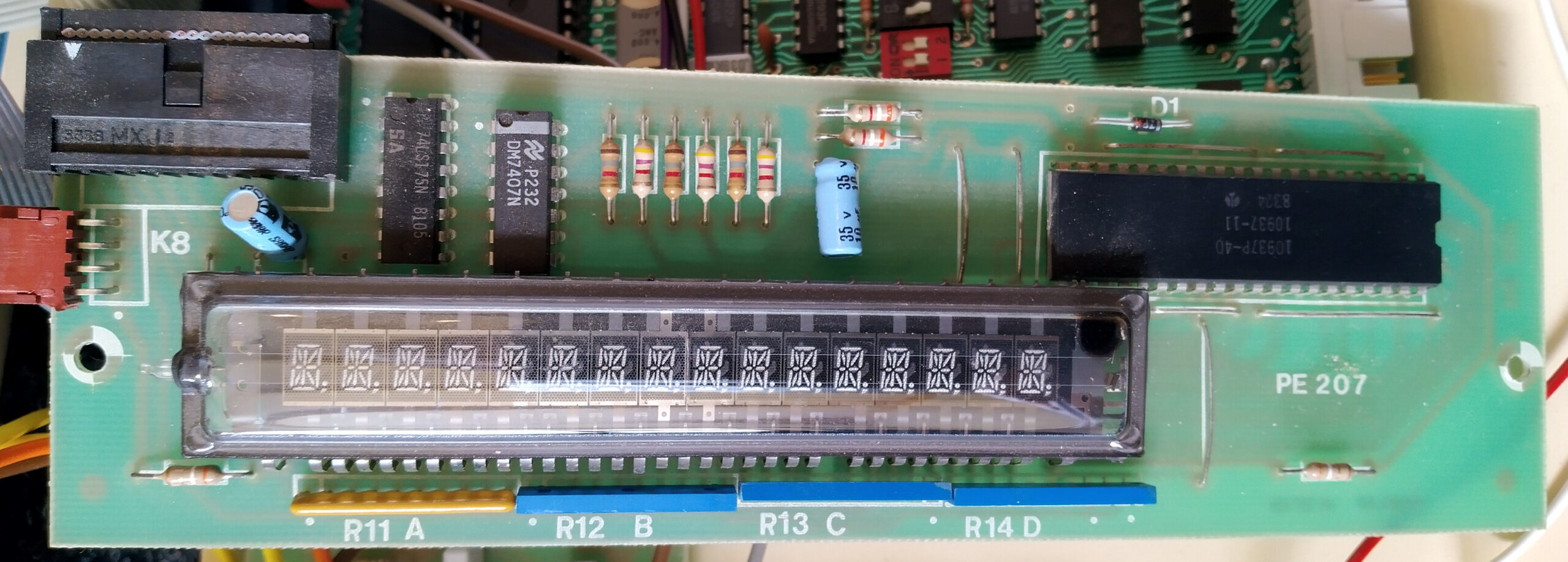
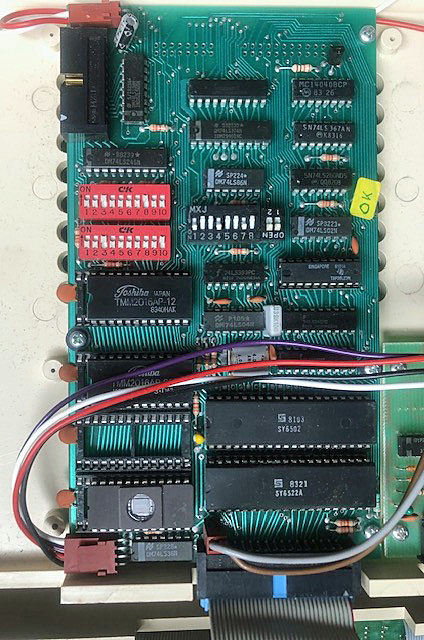
Armin Hierstetter bought it and send me the following photos.
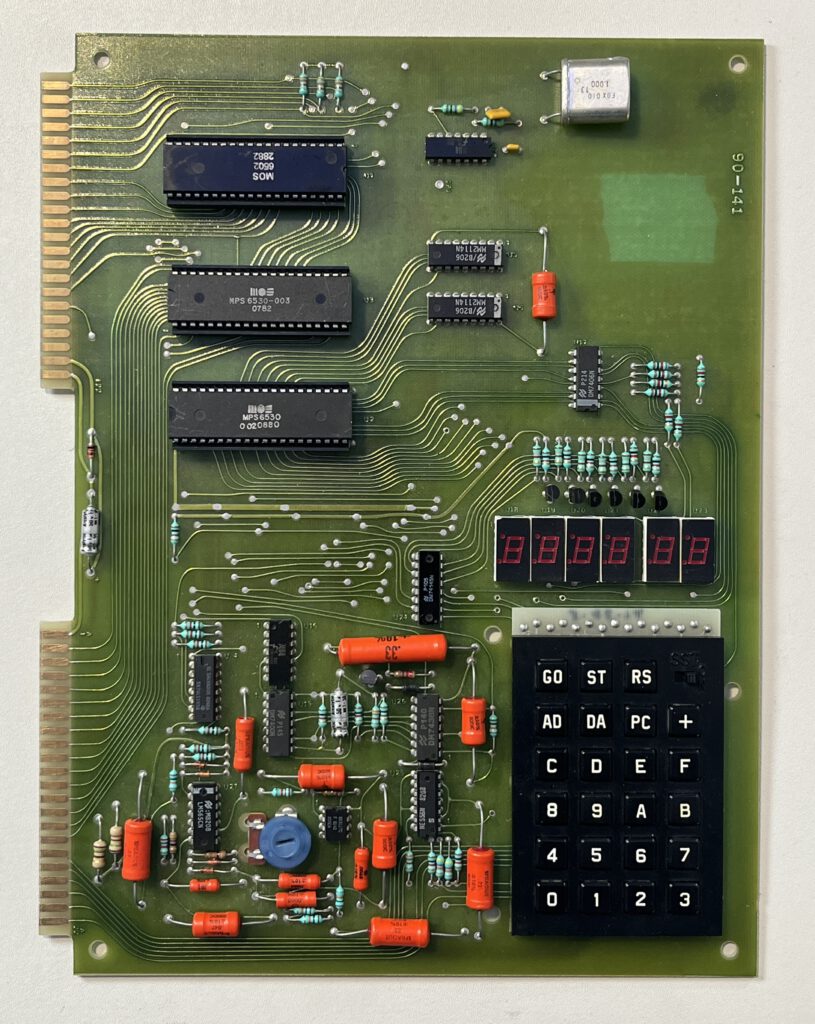
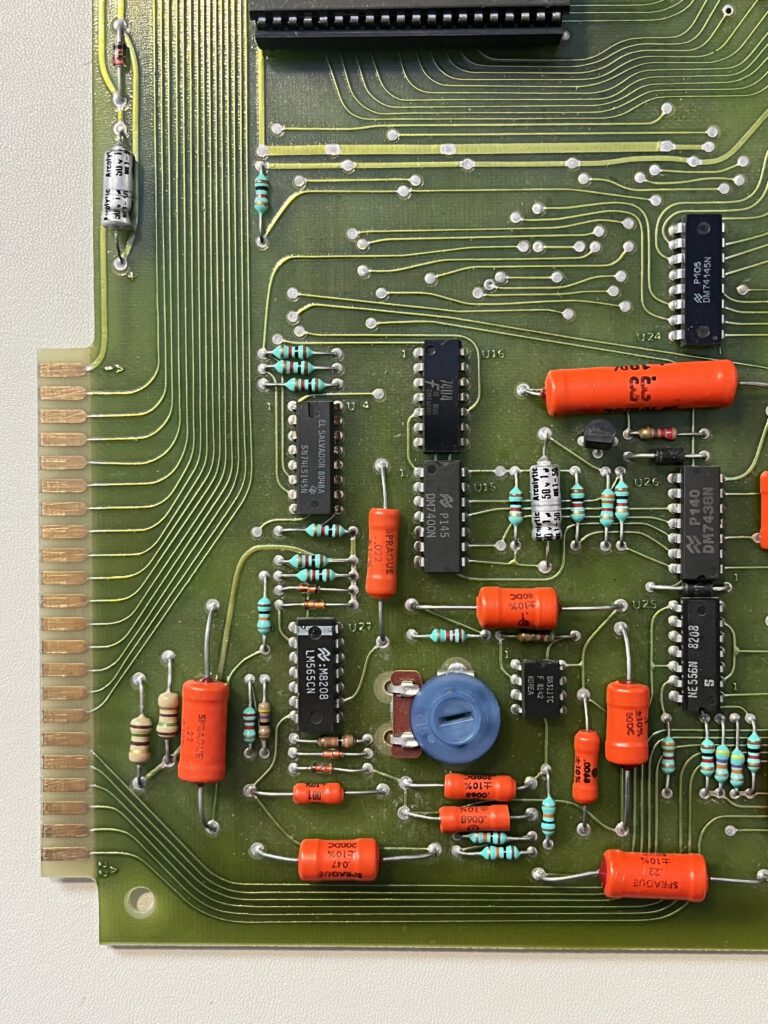
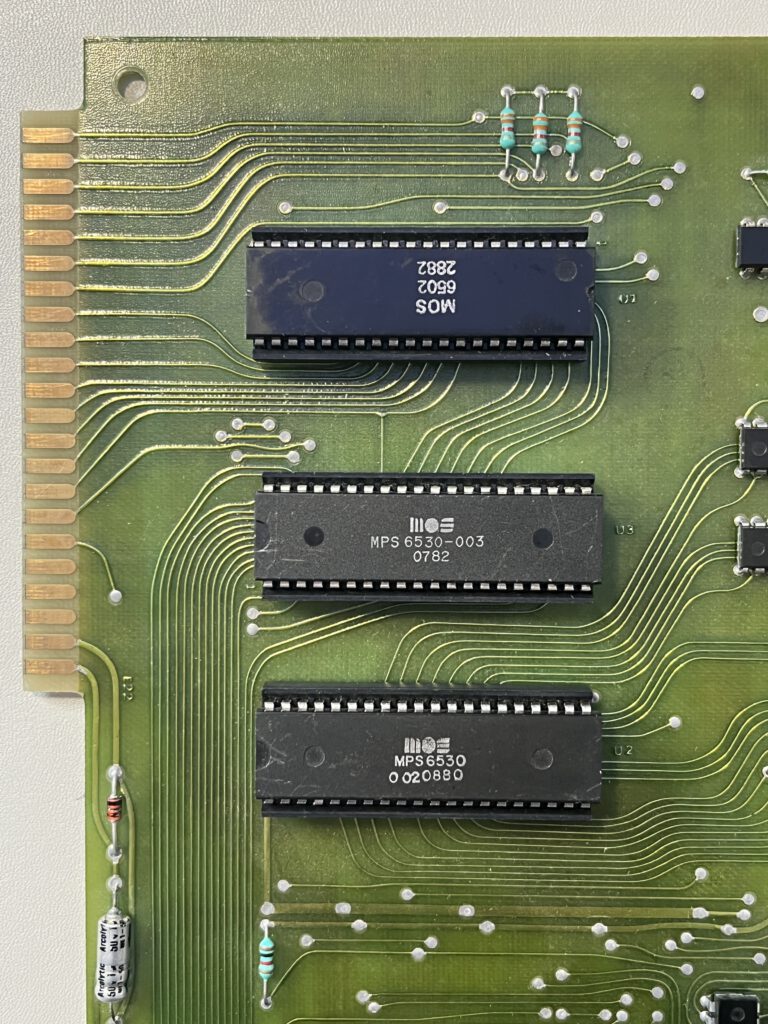
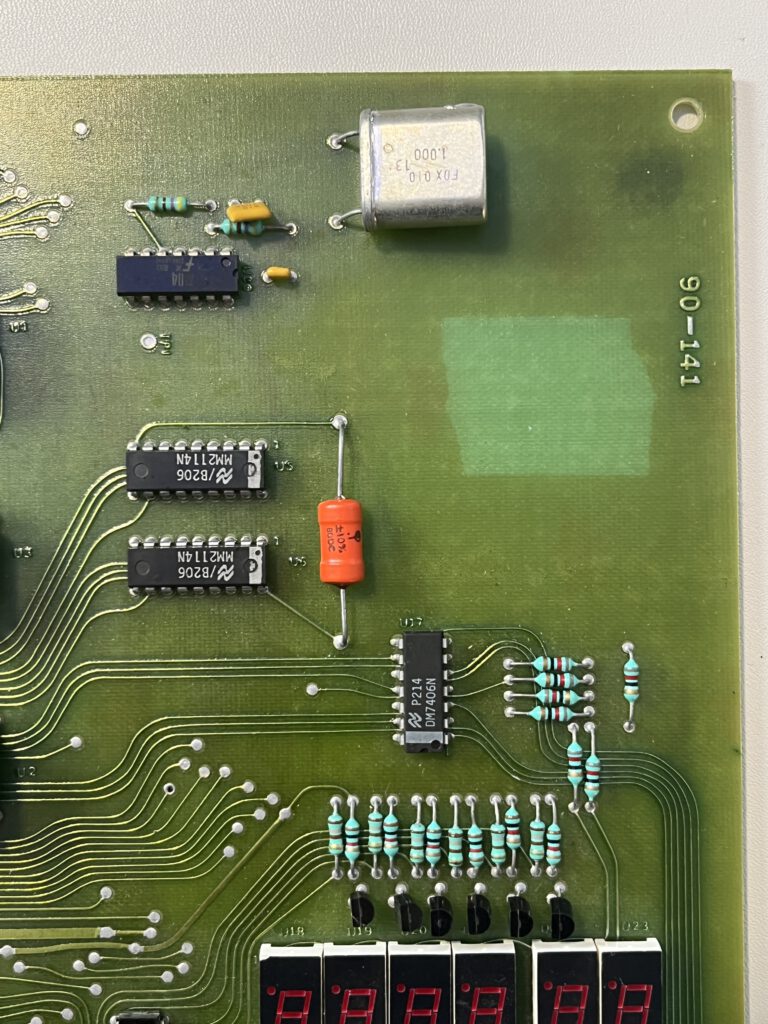
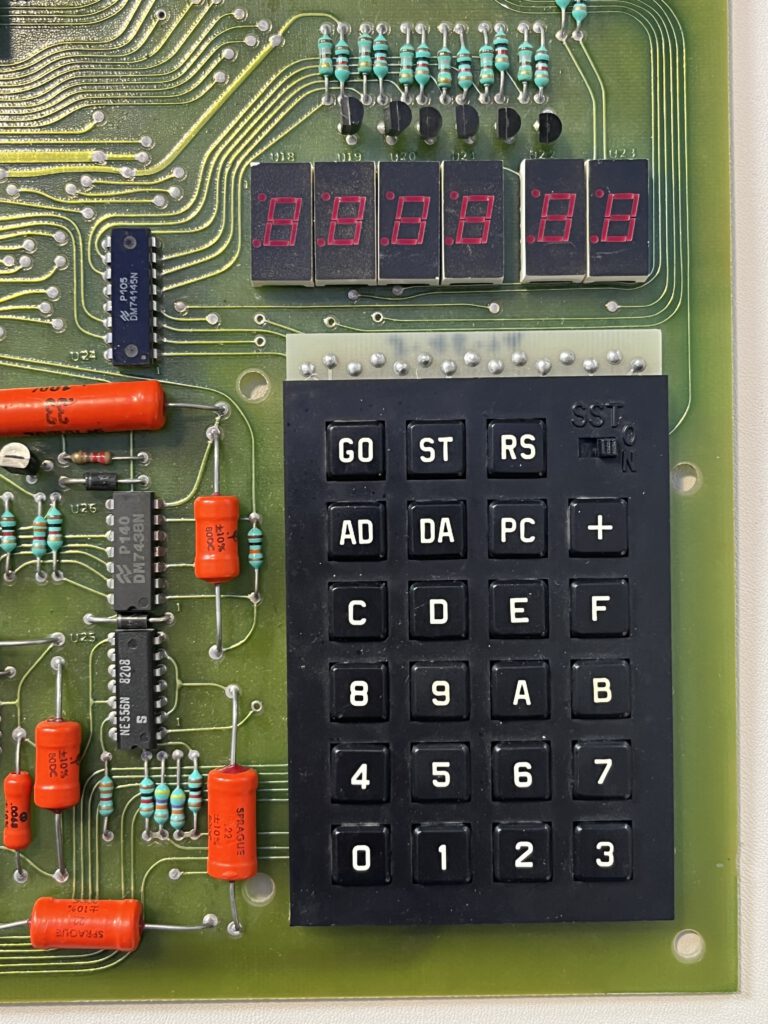
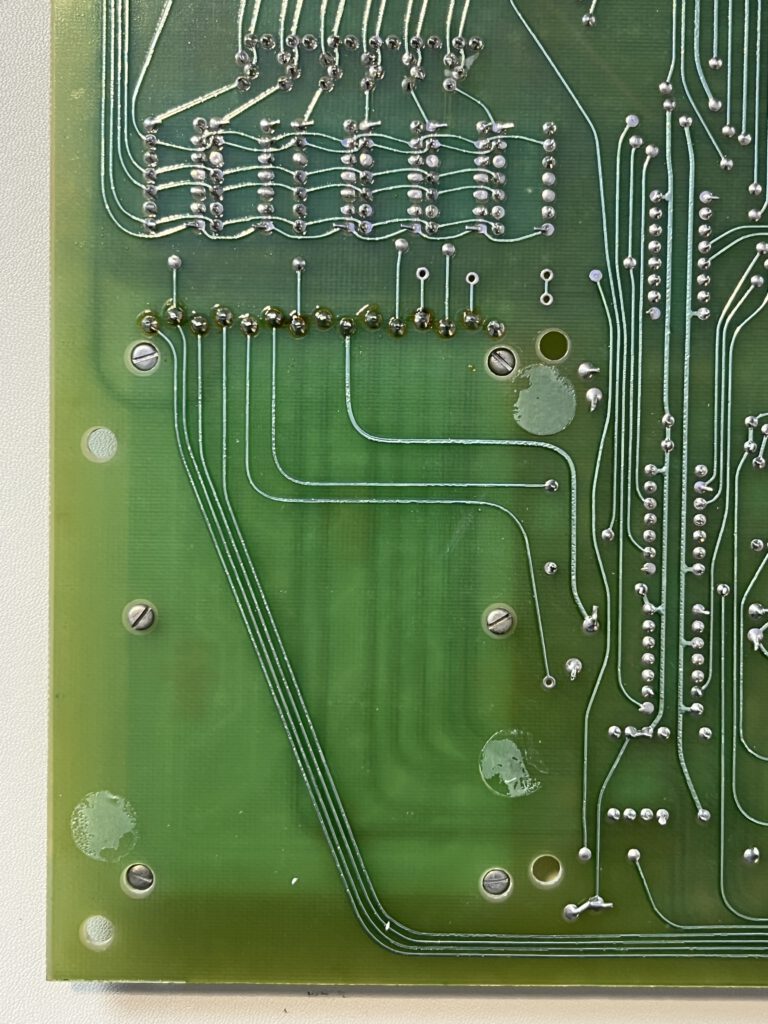
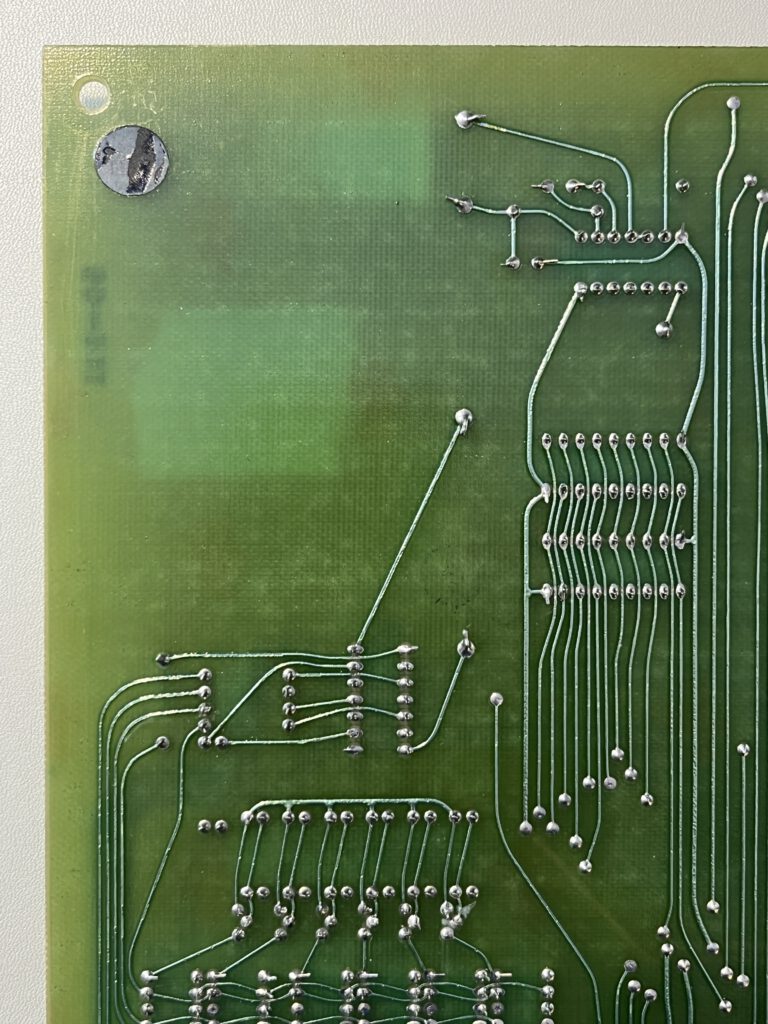
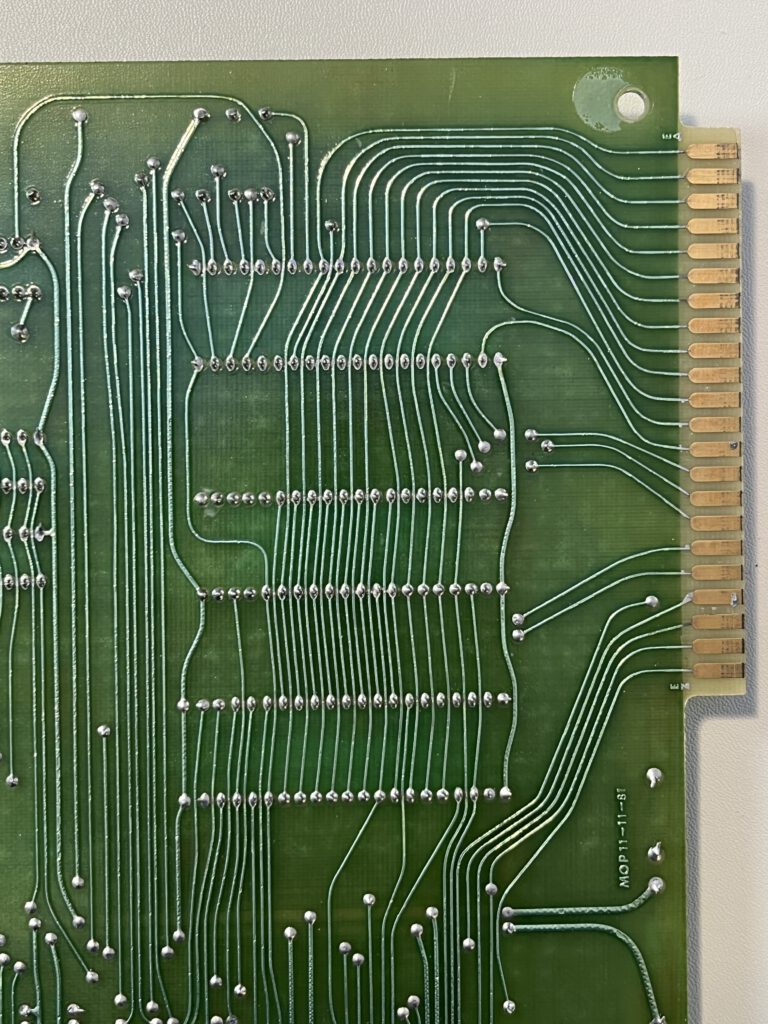
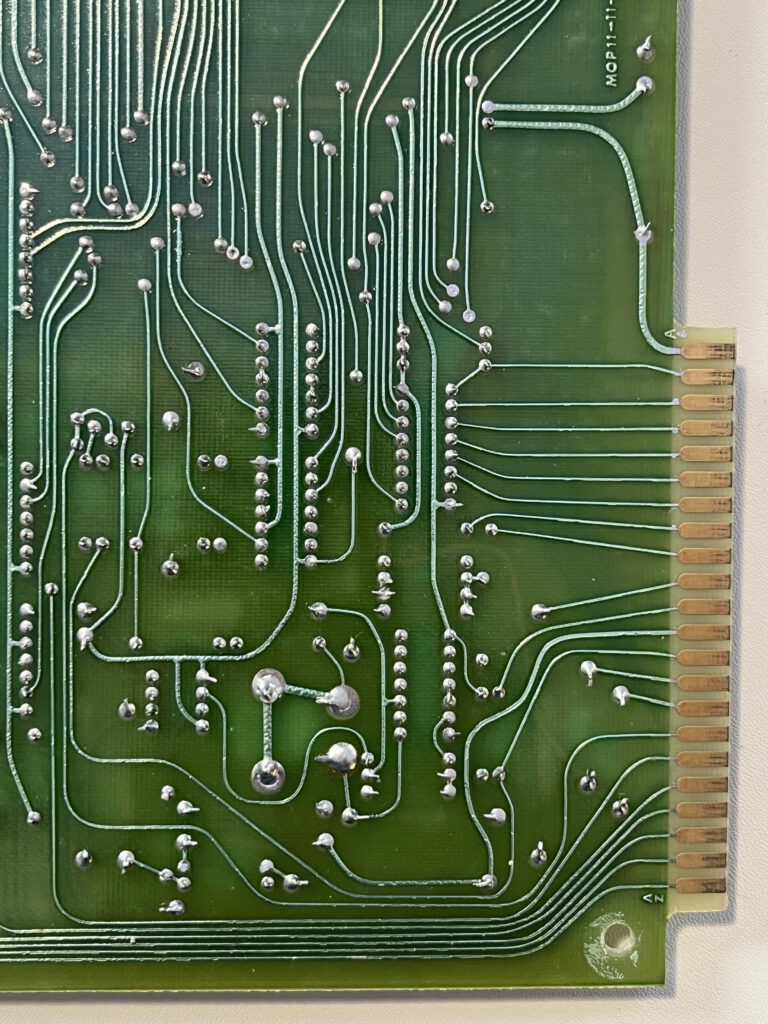

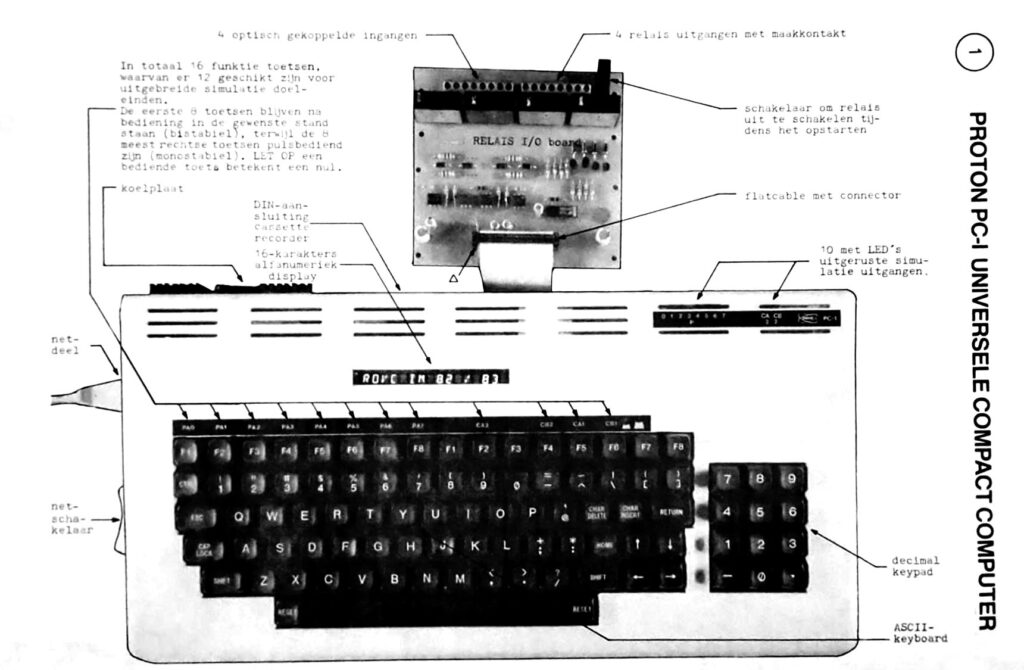
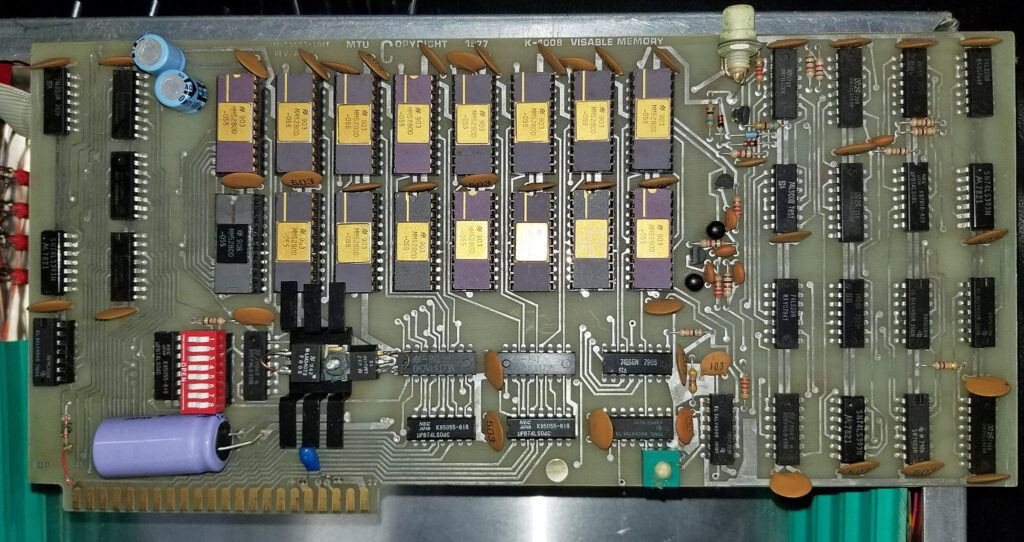
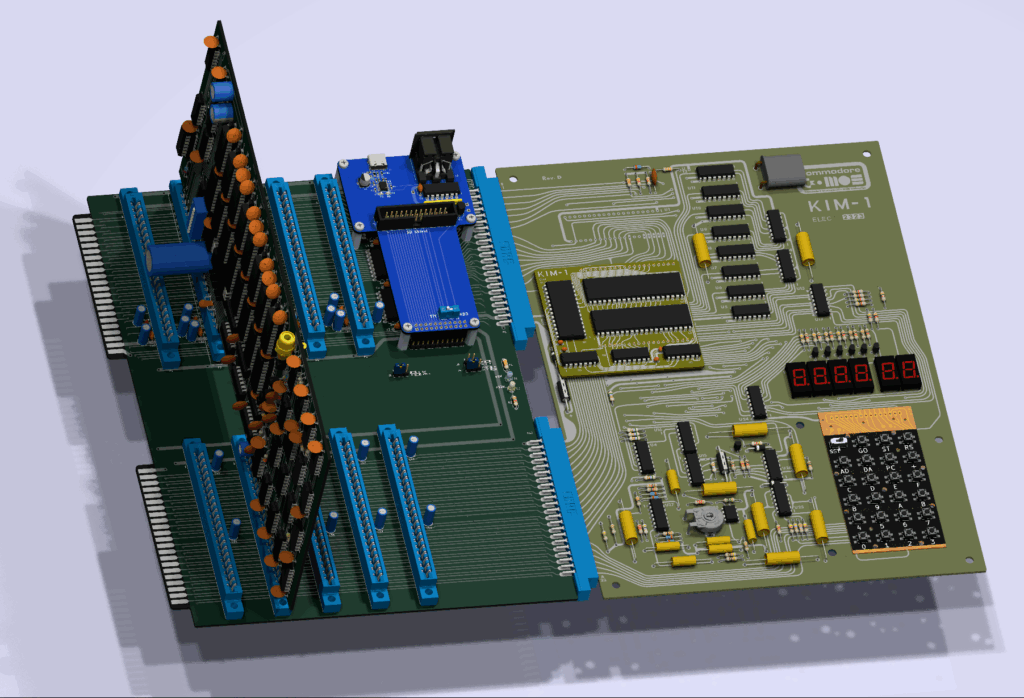
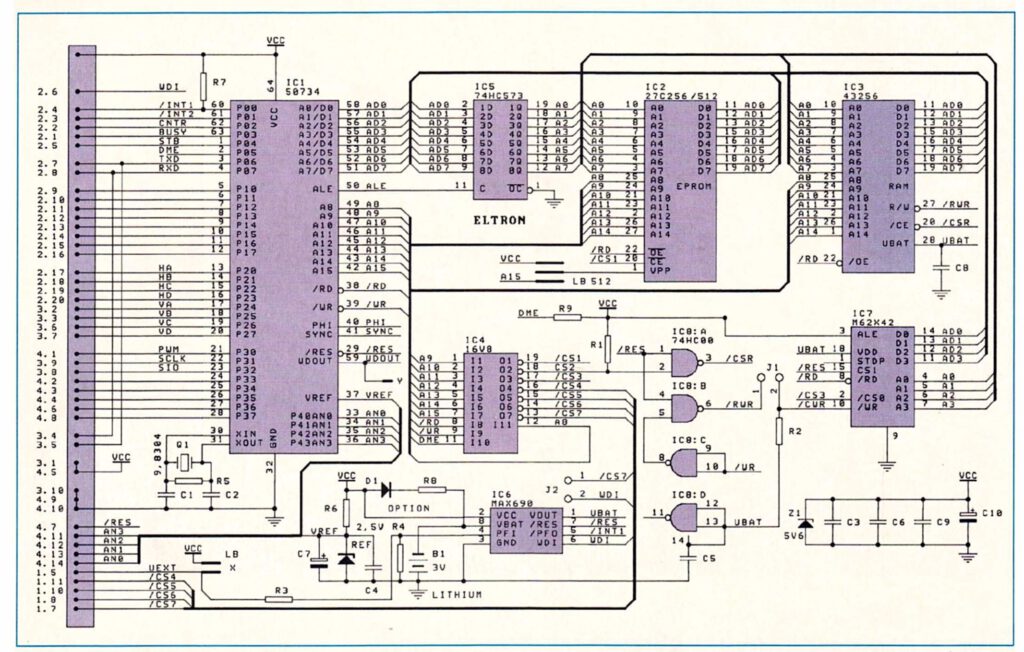
 A full size keyboard, a 6502 at 1 MHz, a VIA 6522 and optional cards for extra ROM (with Basic), video display cassette interface.
A full size keyboard, a 6502 at 1 MHz, a VIA 6522 and optional cards for extra ROM (with Basic), video display cassette interface.