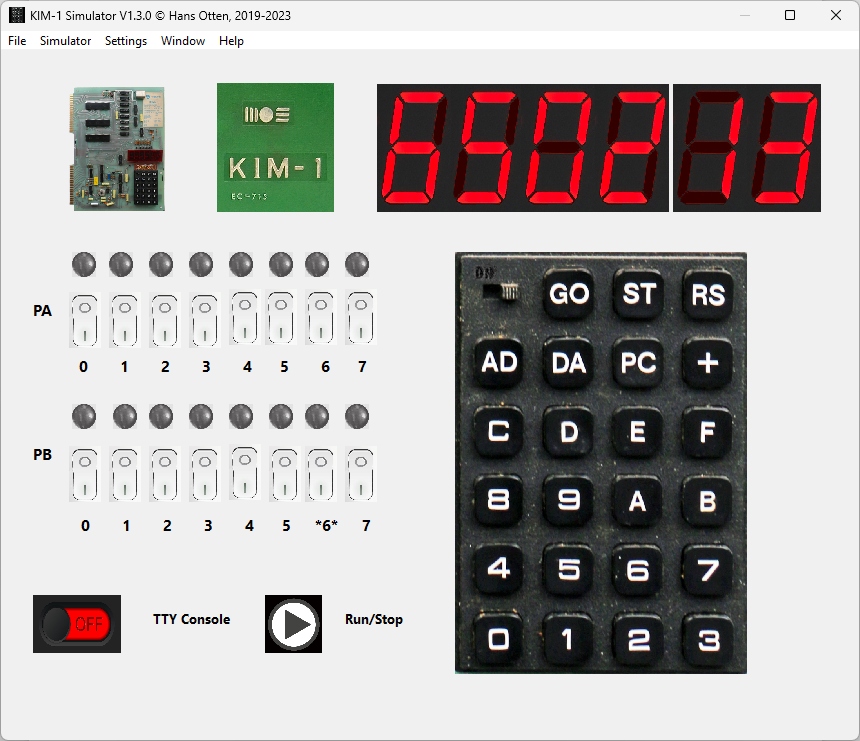
A KIM-1 simulator with the look and feel of the KIM-1 and a debugger to look ‘inside’
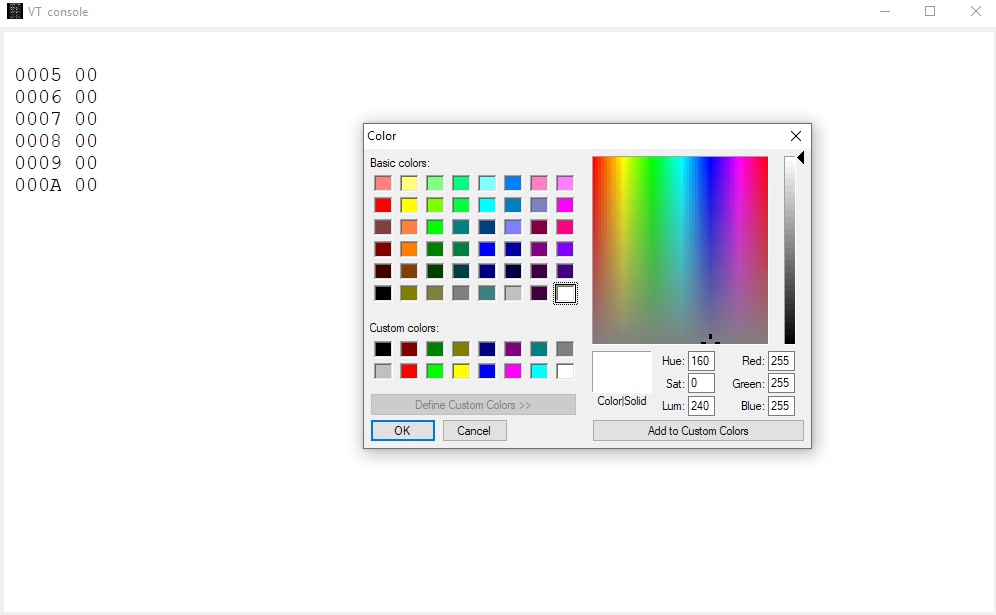
Console, with choice of colors of font and background:
KIM-1 built in ROM tape load and save:
Downloads
Setup for Windows and Ubuntu and Raspberry Pi 5
Source (requires Lazarus IDE 2.x))
Bundled with Conversion 8 bit hex formats utility, to convert to/from various binary files like MOS Papertape, Intel Hex, Motorola S-record and more.
KIM-1 Simulator
Hans Otten, 2019- 2024, Version 1.4.0
Contents
- Introduction
- Installation
- How to use
- Example programs
- Load and Save memory
- Console
- The debugger
- The profiler
- Focal and suppress echo
- Compile from sources
- MTU K-1008 Visible Memory
- Use the Apple 1 monitor (Wozmon)
- Changelog
Introduction
The KIM-1 simulator is written for my personal use to aid me in developing and testing software for the KIM-1. It is not meant to be a cycle exact complete KIM-1 emulation. Instead it shows as much as possible what is happening inside. So do not expect it to run the typical KIM games on the LED and Keypad.
Just for fun and a tribute, it looks and feels and functions as a real KIM-1. The debugger is what the purpose of this program is. The program is developed on Windows 10 (32 bit executable) and tested and compiled on and Ubuntu . Since the source is available, it will run anywhere Lazarus IDE is available.
What is simulated
- 6502 or 65C02 CPU (only documented behaviour)
- KIM- LEDs and keypad
- TTY in and out with TTY console
- 6530-002 and 6530-003 ROM
- The suppress ‘echo TTYecho’ hardware
- The TTY/LED input bit
- KIM-1 Tape load and save ti audio
Limitations
What the KIM_1 Simulator does not do as the real KIM-1:
- Light the LED segments from the RRIOTs outputs. Instead the SCANDS routine is intercepted and the LEDs show the hex output of location F9 FA FB.The simulation is not cycle exact enough to perform the KIM-1 way of flashing the LEDs. So some First Book of KIM type programs will not work.
- The TTY in and out routines are intercepted and rerouted to an ACIA emulation. See the ACIA routines.
- The upper pages are not mapped to the lower pages as in most KIM-1 configurations. The vectors at FFFA etc are pointing to the KIM-1 ROM vectors, so RESET. NMI and IRQ work.
- Tape hardware is not emulated.
- No hardware single-step via NMI, the debugger has much better facilities for that/
- The CPU runs as fast the host CPU allows, and lets the host operating system do some work like key and display and other applications running and continue the emulation loop until the user stops the 6502 CPU.
The speed is herefore dependent on the host CPU. Running the classic Clock program, showing a HHMMSS clock on the LEDs, on my Intel core I7 one minute real time has the clock show 1 hour 37 minutes.
The CPU is halted every 1000 clock ticks to let the GUI of the program a chance to handle mouse and keyboard and screen updates like the stop key.
This works well on the Intel PC, the Raspberry is sluggish to unusable in responding to GUI events if in keypad/LED mode. Dropped form distribution! - The CPU emulation may not be perfect, only valid and documented opcodes are implemented, especially ADC and SBC have many, not emulated here, undocumented issues.
- IRQ handling is not present in this version, see planned enhancements. NMI key works, as does Reset.
Enhancements
The KIM-1 Simulator is a KIM-1 with:
- 6502 or 65C02 CPU (make the choice in the Debugger)
- RAM to $1400
- RAM from $2000 to $E000
- ACIA 6850 at $1600 (equal to Corsham’s I/O card)
- ROM at $F000 with ACIA routines
- Pages E and F are not mapped to page 0 and 1 as in most expanded KIM-1’s.
- LEDs and switches to the user RRIOT Port A and B
- Switch between TTY and LED/keypad
- Emulation of the hardware echo of TTY console input, and echo suppression trick
To do, planned expansions after version 1.0
- IRQ and 6530 timer support
- Testing and bugfixing
- Better documentation …
Installation
Windows
Run KIM1SIMsetup.exe or place the files KIM1SIM.EXE + KIM1Simulator.html file in a folder of choice.
For high DPI screens change the Properties of the KIM1SIM.EXE, Compatibility settings,
– Change high DPI settings,
– check high DPI scaling Override,
– scaling performed by “System(enhanced)”.
Ubuntu 20.04.3 LTS
Execute KIM1SIM from the Ubuntu folder. Works fine on a modern PC.
Note that the font used is Courier New. Install ttf cour.ttf on Linux in .home
Other platforms
If Lazarus is available then install Lazarus (Version 2 or higher) and build from source.
No extra packages are required, just a standard Lazarus.
Open the project KIM1SIM.LPI and do RUN – Build to get an executable.
This may work on MacOS. It seems not easy, Lazarus is not that stable on MacOS it seems.
After installation
Start the KIM-1 Simulator and choose Settings to
– set the default working directory. Otherwise files may appear at locations you do not want!
– select the keyboard layout in the console (Geman and US International for the moment)
How to use as KIM-1
Start the emulator main program and push the ‘Run’ icon. Then press the RS key on the keyboard (or type R).
After that the LEDs awake and the keyboard is operational as a KIM-1.
[0] to [F] - Sixteen keys used to define the hex code of address or data [AD] - selects the address entry mode [DA] - selects the data entry mode [+] - increments the address by +1 but does not change the entry mode [PC] - recalls the address stored in the Program Counter locations (PCH, PCL) to the display [RS] - causes a total system reset and a return to the control of the operating program [GO] - causes program execution to begin starting at the address shown on the display [ST] - terminates the execution of a program and causes a return to the control of the operating program
Besides pressing the keys on the KIM keybaord on the screen you can also use the PC keyboard:
0-9 : key 0 - 9 a-f : key A - F A-F : key A - F + : + A : AD D : DA P,p : PC G,g : GO S,s : ST R,r : RS S,s : ST
Console
Press the TTY switch and run/stop and you have a console terminal. The KIM-1 teletype commands now work and also programs line KB9 Basic can be used. See the Console chapter below.
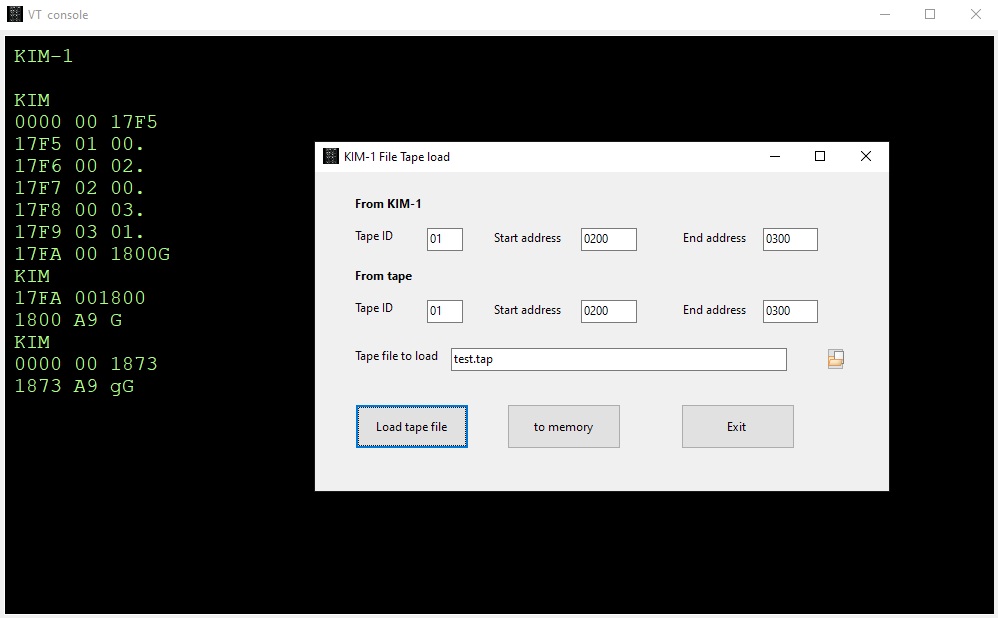
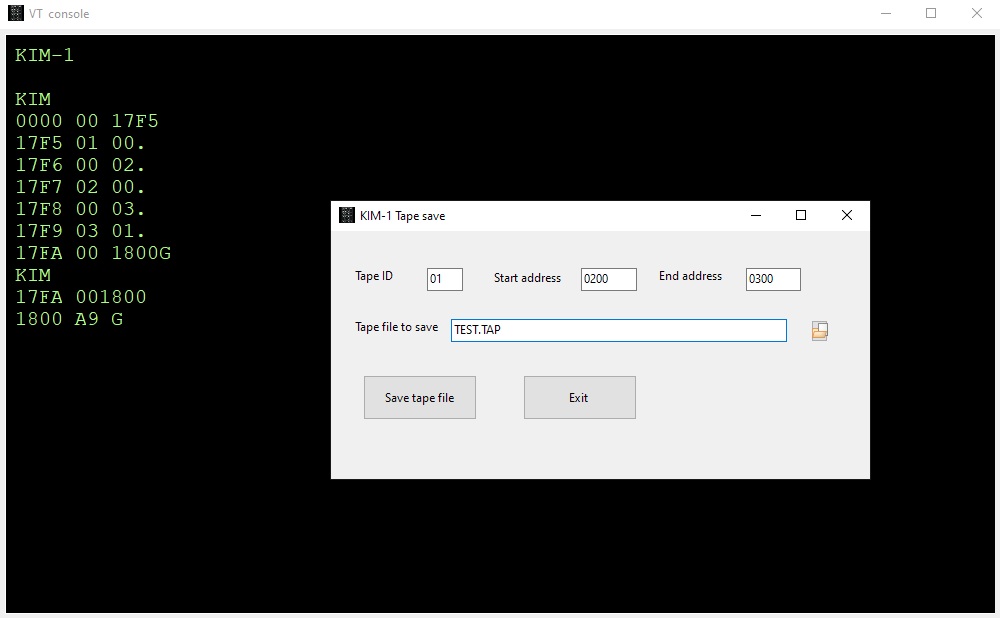
KIM-1 Tape load and save
The KIM-1 tape load ($1873) and save ($1800) programs are emulated.
Fill in the tape ID and optionally start and end address as documented in the KIM-1 User manual.
Start the Save at $1800 and the load at $1873 with the KIM-1 monitor.
You will be prompted for file to load or save.
Default working directory and other settings
Use the menu Settings to dipslay the possible settings that survive sessions.
– Set default work folder to choose a folder for all files created or used by the emulator. The settings are saved between sessions.
– Set the preferred keyboard layout (US International German,Belgium (french), others await your input, see below)
Default settings config file : “/home/(user)/.config/KIM1SIM.cfg” or C:\users\(user)\Appdata\local\KIM1SIM.cfg”
Loaded at startup, updated via the Settings menu.
Load and Save
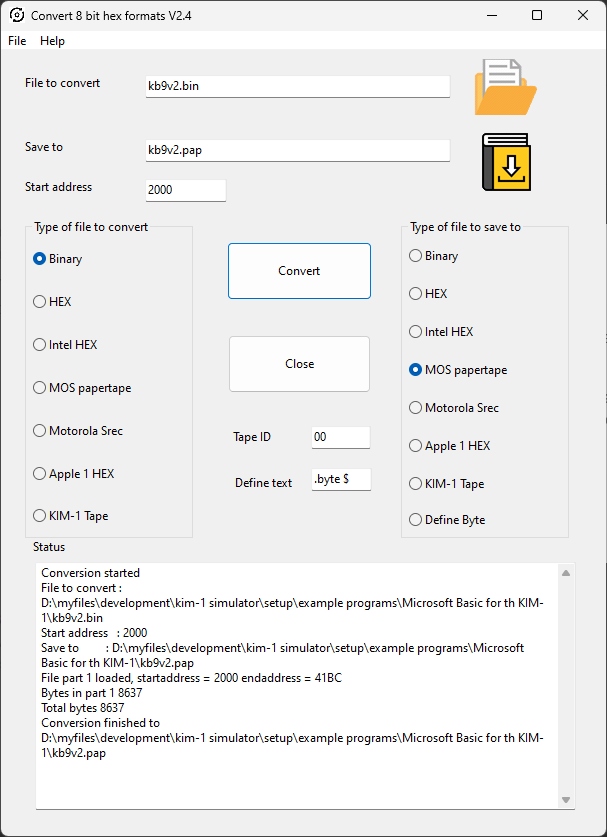
The menu has Load and Save functions, you can load and save to many 8 bit binary formats as MOS papertape, Intel HEX, Motorola S record, binary and simple hex.
The 16 bit versions of Intel Hex etc are not supported.
The Define Type is a text file format suitable for inclusion in assembler source.
The layout is as follows (all in hex)
; <Start address> - <end address> <define text> $<hex data> .. where <define text> is what you fill in the Define text entry, may be empty. Example: ; 1800-1805 .byte $A9 .byte $AD .byte $8D .byte $EC .byte $17 .byte $A9
TTY console mode
Press the TTY console switch to let the KIM simulator use a glass teletype in a console window. The standard KIM user interface is shown, see the manual how to use.
Note: set the PC keyboard to CAPS Lock, only uppercase is used in the KIM monitor.
Note the menu options to record a session, (Load Text to Console) or play (Save text from Console, followed by Stop saving text ) a text file in the console.
This is in fact the same functionality as a teletype with high speed papertape punch or reader. You can use this to load and save Basic programs as ASCII text files. Or use the KIM-1 tape routines built in KB9 Basic!
The console
The console is an emulation video terminal (ANSI color, subset) connected to an ACIA (a Motorola 6850) in the KIM-1. The KIM Monitor is patched to send or receive via the ACIA and is transparant to the user of the KIM-1 I/O routines (even the quirlks like flags and returned register values!)
Keyboard input, when the console window has focus, is sent to the serial input of the ACIA. No local echo. The KIM-1 monitor only accepts uppercase (hint: Caps lock!), user programs are free to use upper or lowercase.
Characters sent tot to ACIA output are received by the console window and handled as a VT100 would do, a subset of the ANSI/VT100 is implemented.
All keys of the PC are usable, SHIFT works. Note the translation of codes from the PC keyboard to ASCII characters is for the keybaord choosen in Settings.
Other mappings are possible by changing the routine in console.pas: procedure TFconsole.FormKeyDown
Received characters by the console are handled as follows, a subset of the ANSI set.
Single control character
$01 : CursorHome $04 : CursorRight $05 : CursorUp BS : Backspace TB : Tab LF : LineFeed FF : ClearScreen CR : CarriageReturn $13 : CursorLeft $16 : DeleteToEndofLine $18 : CursorDown DEL : Backspace ESC sequences ESC[K Clear from cursor to the end of the line ESC[0K Clear from cursor to the end of the line ESC[1K Clear from the beginning of the current line to the cursor ESC[2K Clear the whole line ESC[J Clear the screen from cursor ESC[0J Clear the screen from cursor ESC[1J Clear the screen until cursor position ESC[2J Clear the screen and move the cursor to 0-0, defined sprites are removed, loaded bitmaps are kept Insert / Delete ESC[1@ Insert a blank character position (shift line to the right) ESC[1P Delete a character position (shift line to the left) ESC[1L Insert blank line at current row (shift screen down) ESC[1M Delete the current line (shift screen up) Move cursor ESC[H Move to 0-0 ESC[f Move to 0-0 ESC[s Save the cursor position ESC[u Move cursor to previously saved position ESC[(Row);(Col)H Move to row,column ESC[(Row};(Col)f Move to row,column ESC[nA Move the cursor up n lines ESC[nB Move the cursor down n lines ESC[nC Move the cursor forward n characters ESC[nD Move the cursor backward n characters Attributes ESC[m Reset all attributes ESC[0m Reset all attributes ESC[1m bold ESC[4m underline ESC[5m italics ESC[7m Turn on reverse color ESC[27m Turn off reverse color Color attributes color FG BG FG high BG high -------------------------------------------- black ESC[30m ESC[40m ESC[90m ESC[100m red ESC[31m ESC[41m ESC[91m ESC[101m green ESC[32m ESC[42m ESC[92m ESC[102m yellow ESC[33m ESC[44m ESC[99m ESC[103m blue ESC[34m ESC[44m ESC[94m ESC[104m magenta ESC[35m ESC[45m ESC[95m ESC[105m cyan ESC[36m ESC[46m ESC[96m ESC[106m black ESC[37m ESC[47m ESC[97m ESC[107m FG = foreground BG = background High = higher intensity Note that setting colors is implemented in a limited way. Combining attributes and fore/background in one Escpe sequence is not supported If you want to use for example ESC [1;31;104m (bold, red foreground, blue background) you will have to use ESC[1m ESC[31m ESC[104m Printable character (>= $20): placed on screen where the cursor is, cursor moved to next position Wrap around at end of line, screen scroll up when bottom line is reached
Console and the keyboard
Handling different keyboard layouts and platform independent development is a nightmare! The Console in Version 1 and below is built for the US International keyboard, the only type I use.
SInce then some more keybaord layoyts are added, you can select form the Settings.
This means the key code translation is fine for a-z, A_Z, 0-9, with NumLock also for the numeric keyboard, backspace, delete and othr control characters. Fine for the KIM-1 monitor.
The key code translation is now not optimal for keyboards with other layouts, characters like []{}\|;:'”,<.>/?!@#$%~^&*()_+ are possibly mapped wrong.
This can be fixed in a newer version by letting the user select a keyboard layout. But I do not have all those keyboards and the information on the internet is confusing.
So I built a test program to let you help me: Testkeydown. Fill in the type of your keyboard, press at least the []{}\|;:'”,<.>/?!@#$%~^&*()_+ keys, et Num Lock and press the numeric keyboard.
Save to the file keydowntestfile.txt and sent it to me at h.otten (fill in here at sign) hansotten.nl so that I can add your variant to the Simulator.
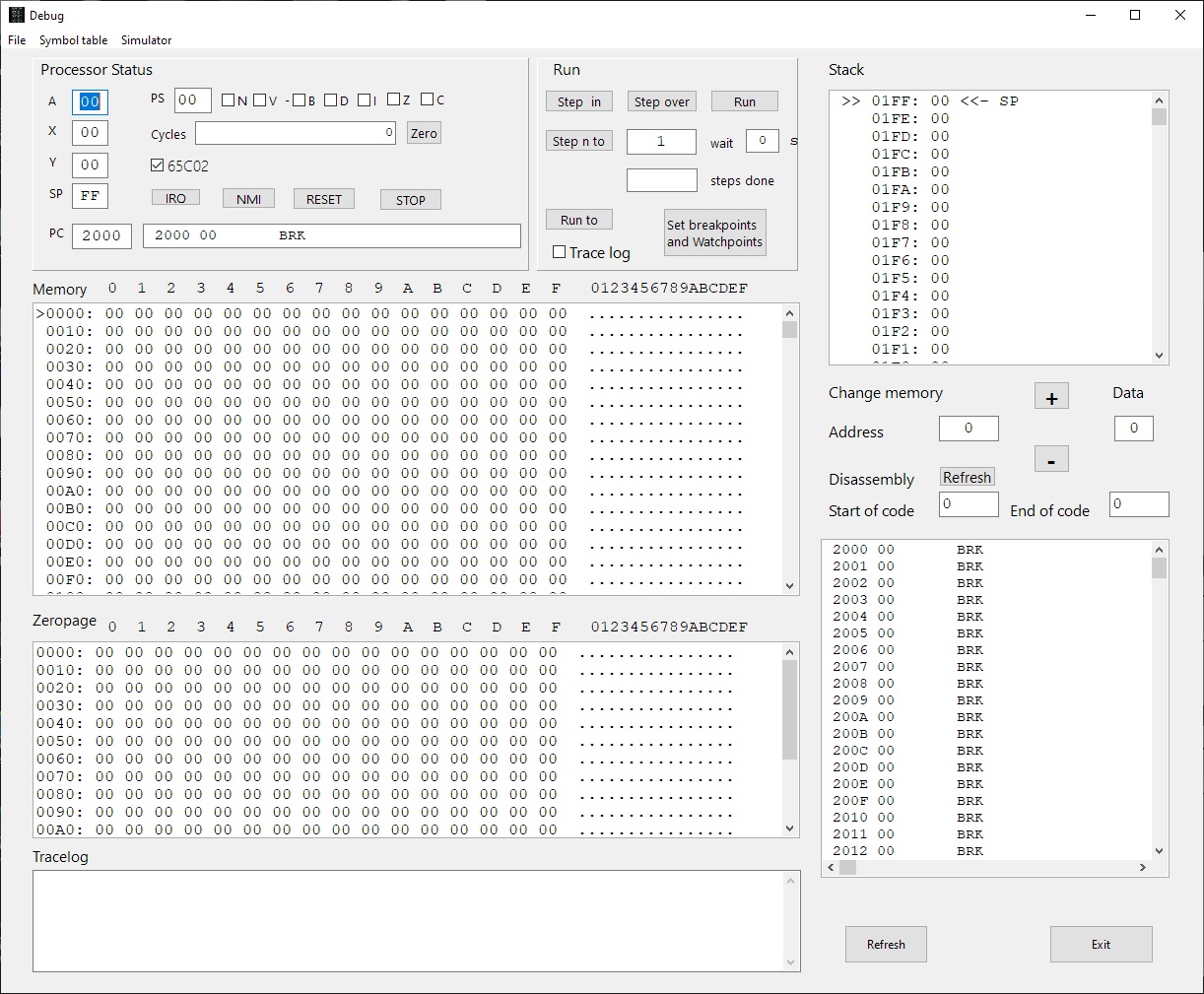
The debugger
From the menu Simulator choose Debugger to show the debug window. This windows has step/single step/run buttons, shows the registers and flags, zeropage, memory and the stack. The Trace logfile facility may store a trace of what happened.The disassembler part shows a disassembly.
Several refresh buttons let you update the current state of the machine.
Single step, RUN, trace log
First set the PC to the first instruction of the program to test.
- Step in: execute next instruction
- Step over: execute next instruction but skip JSR subroutines
- RUN: execute at maximum speed ( wait 0) or slow (wait x seconds between steps), use the STOP button to halt execution
- Step n: execute n instructions full speed
- Run to: execute instructions full instructions until the breakpoint or watchpoint location is reached or STOP pressed
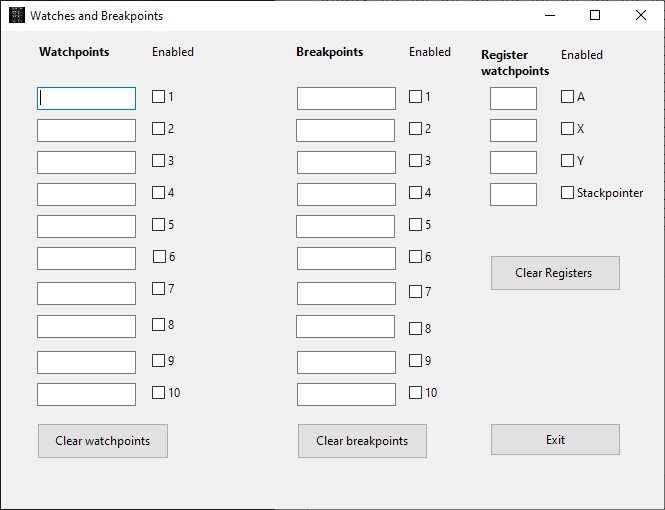
- You can set 1o code breakpoints, 10 memory watch points and wacthpoinst on registers A,X,, Y and Stackpointer, press the Breakpoints and Watches button to show the form to fill in as desired.
- Trace log on/off: first set the Trace log file directory from the file Menu, then use any Step to have every instruction logged with status in the logfile and the tracelog.Note that this slows down execution a lot and the files can become large. So clean up regularly!
The file name of the log is set to KIM1SIMtrace(datestamp).log.
From the Search Memory you can Search with hex 1,2 or 3 bytes in memory (leave unwanted fields blank), Fill memory and Copy/Move memory.
With a fill byte you can replace the moved bytes, leave the field empty to leave the original value.
Symbol table and the disassembler
The disassembler shows locations/labels in hex format. If the assembler symbol table is available (TASM can produce that as blank delimited list) you can load it and do some symbolic disassembly.
Load and show the symbol table from the menu “Symbol table”. Supported symbol table formats: TASM 32 bit and CA65 (part of CC65 suite).
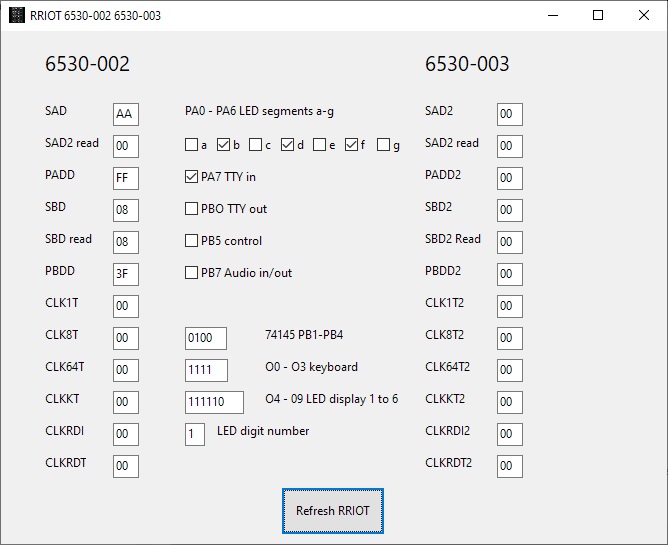
RRIOT status display
From the menu Simulator choose RRIOT to show a windows with the current RRIOT status or you can enter new values for the various registers.
Press Refresh to update to the current state, it is not updated realtime.
The 6530-002, responsible for the KIM-1 hardware, is decoded to the relevant in/output bits.
Note that the simulator does not perform the KIM-1 LED/key functions this way. Code for output to the LED displays is currently present but commented out in the source.
Timing limiting is essential for this to work, the simulation now runs as fast as the host CPU can deliver.
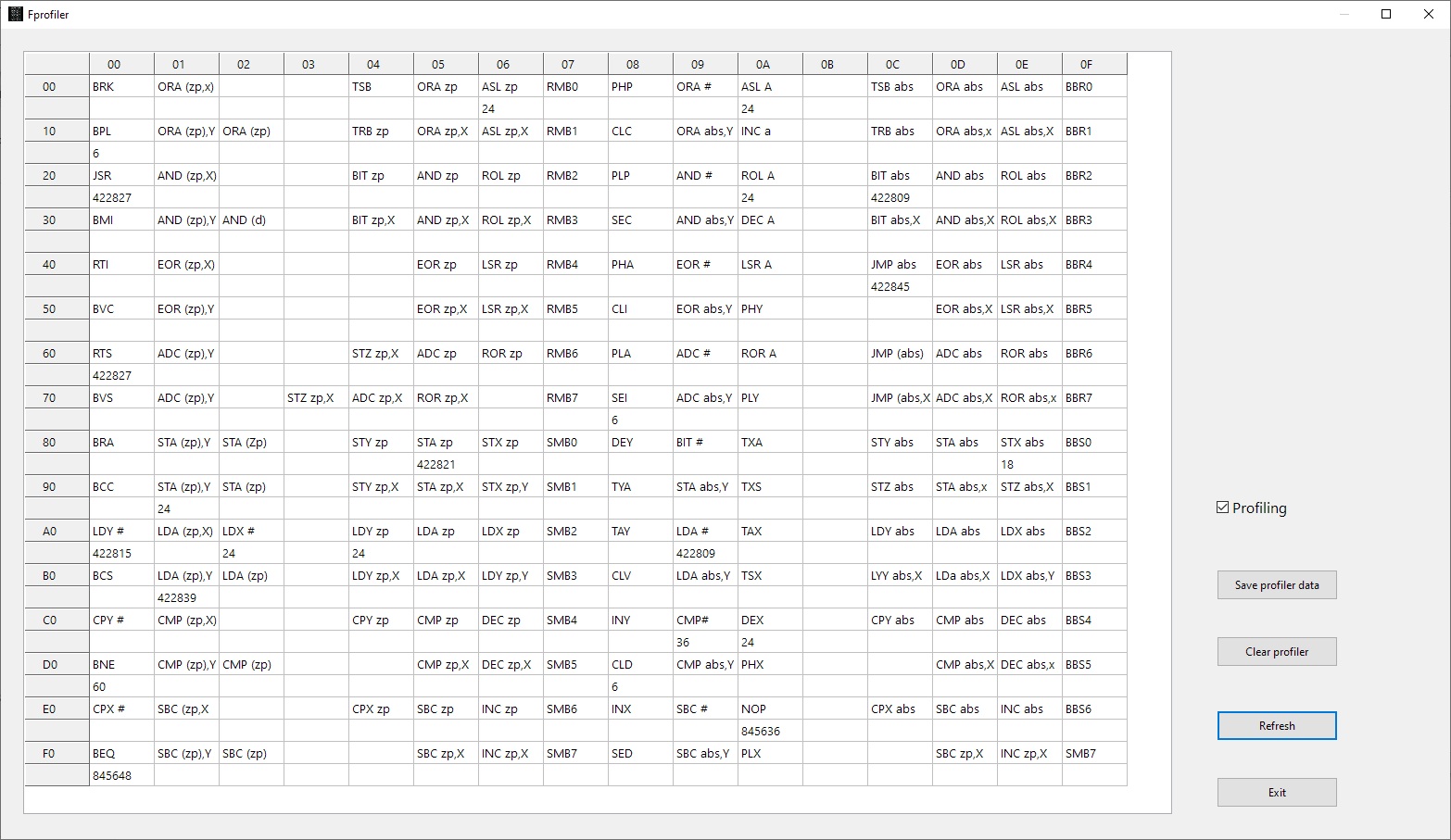
The Profiler
Available from the ‘watches and breaks’ form or from the Window menu
This facility keeps track (once activated with the Profiling Check box) how much an instruction is executed,
Independent of the debugger, always available.
Use the Refresh button to see the current state, not automatically updated so it is no a high performance hit.
Any opcode, from o to 255, is counted. The display shows the maximum 65C02 instruction set.
You can save the profiler data to a CSV file, with instruction mnemonic and number of times executed per line.
Invalid instructions are marked as ‘Unknown’.
Focal V3D from the KIM-1 Software page
Focal V3D, an interpreter modeled after the DEC PDP-8 Focal interpreter runs on the KIM-1 and on the Simulator.
This program uses a trick to suppress the echoing of charaters typed on the KIM-1 TTY hardware. And another trick to get a hash/random number.
After loading both zeropage and program code, start at $2000. But first go to sSettings and choose Focal Break testing.
Only when running Focal! Set to Normal break testing for e.g. MS Basic. This setting is not saved, and resetting the emulator makes the setting to Normal.
Example programs
In the Setup archive a folder with TTY programs are collected. Note that manuals etc are on the Retro website.
kb9.bin load 2000 start $4065 Microsoft KIM-1 Basic 9 digits (upercase only, set 00F1 to 0)
kb6.bin load 2000 start $3D50 Microsoft KIM-1 Basic 6 digits (upercase only, ROR instruction patched + CLD)
kb9V2.bin load 2000 start $3F8E Microsoft KIM-1 Basic 9 digits (upercase only, ROR instruction patched + CLD)
kimGFX.BIN load 2000 start 2000 Demo for K1008 video display Dave Plummer
kimGFX1.BIN load 2000 start 2000 Demo for K1008 video display Dave Plummer
kim1sim6502test.ihex start 2000 65(C)02 opcode test (lower case y/n)
Focal folder
Set in Settings Focal3D break setting
focalzp.bin load $0000
focalm.bin load $2000 start 2000
Printing disassembler
PRDISV3.PAP start B000
Compiling and building the simulator from source
Prerequisites
- A modern PC and operating system. Windows 10/11 is where the software has been developed, Ubuntu are tested and binaries included.
- Development (Compile and run everywhere!) with Freepascal and Lazarus IDE, see https://www.lazarus-ide.org/
Any Lazarus version above 2.0 will be OK. - The archive with the KIM-1 Simulator sources KIM1SIMsourcesxxx.zip.
- Unpack in a folder, avoid blanks in folder and filenames
- Start the IDE by clicking on KIM1SIM.lpi
- Build with Run – Build
- On Windows a Setup installable can be made with Inno Setup, KIM1SIM.iss and compile with Inno Studio.
Note that the font used is Courier New. Install ttf cour.ttf on Linux in .home/pi/.fonts to prevent substitution with artefacts
The include files with KIM ROM and 6502 code
If and when the ACIA routines and other routines in the KIM1SIM ROM are altered you need to rebuild the KIM1SIMrom.inc file.
Subfolder ‘romtoconst’ contains the binary of the original KIM ROMS (6530-002.bin, 6530-003.bin) and the additional ROM binary with ACIA routines (kimsimrom.bin).
The .inc files for the compilation of the KIM1SIM, to be placed in the main folder, are created with the program creatINC.exe, a console application (source included here).
Copy the the tree .inc files to the main folder and compile the KIM1SIM program again.
D:\myfiles\development\kim-1 simulator\romtoconst\creatINC.exe kimrom002 include file created kimrom003 include file created kimsimrom include file created
Folder KIM-1 assembler sources
Here you find assembler sources of various tests. Assemble with TASM, included in the folder. See TASM.HTML for information.
It is convenient to compile from an editor like Notepad++, plugin NPPEXEC
with command to create intel hex file
"D:\myfiles\development\kim-1 simulator\KIM-1 assembler sources\tasm" -65 -x3 -g0 -s $(FILE_NAME) $(NAME_PART).ihex $(NAME_PART).lst -s $(NAME_PART).sym
or to create a binary file with
"D:\myfiles\development\kim-1 simulator\KIM-1 assembler sources\tasm" -65 -x3 -g3 -s $(FILE_NAME) $(NAME_PART).bin $(NAME_PART).lst -s $(NAME_PART).sym
Note that also symbol files are generated which can be read in by the debugger in the KIM-1 Simulator.
- kim1sim6502test.asm : The 65(C)02 test, a program that runs on the TTY console
- kimsimrom.asm : the source of the KIM-1 Simulator ROM at $F000 with ACIA support for KIM-1 TTY in/out
- Various snippets used to test the CPU emulation
MTU K-1008 Visible Memory
The MTU Visible Memory is a memory mapped video display made by MTU.
See the K-1008 Manual how it works.
Enabling it will display a form on which the video memory is shown (according the packing of the pixels in bytes, see the manual).
Use the Settings from to enable or disable (default) the K-1008. The base address in memory can be set to what the original board allowed with jumpers.
The K-1008 display can be resized from 1x to 3x. Larger means a slower display, not much effort has been put in making it display fast.
A fourth option is to choose for a correct aspect ratio.
Note that the pixel only appears on screen when the corresponding memory location is written to by the CPU. Use Refresh in the Debugger to force the display.
Using MS Basic: the interpreter will detect the video memory as normal memory. No harm done, MS Basic does not support the K-1008. The memory test of MS Basic is visible on the K-1008 display!
There are several ways an image can be loaded to the K-1008 video display:
- Load a K-1008 formatted binary file into memory. It will show on the K-1008 display if enabled via Settings.
- The Refresh button in the debugger will also refresh the K-10008 display from memory
- With a C header file. see below
How to make a C Header image file with threshold
- Choose a high contrast image
- Load the image in GIMP (a freeware image processing app for Windows, Linux etc)
- Scale the image to 320×200 exactly(have the ties between the dimension windows untied)
- Use the Treshold tool to convert to black and white, play with the settings until it looks good
- Export to, choose the C header file format, a file
- This file can be loaded with the File menu entries of the KIM- Simulator main window and Debugger
- The file is converted if you load in it into memory
- If you have the K-1008 display on (see Settings) it will display it too
- Now you can save the image if you wish with the ‘Memory to file’ menu entries
Make a C Header image file with dithered images
- Open image in GIMP
- Crop the image to 320×200 or a multiple like 960×600
- Image – Scale the image to 320×200
- Image – Mode – Indexed to black white palette Floyd-Steinberg (normal)
- Image – Mode – RGB
- File -Export As Select file type – C source header
- Export
Note there is a command line program in the folder K-1008 load C Header , called LoadK1008 that converts a C header image file to a K-1008 formatted binary.
D:\k1008\LoadK1008.exe h LoadK1008 is a program to convert a 320x200 C header file from GIMP to MTU Visable memory K-1008 image LoadK1008 <C header filename> <K-1008 binary filename>
Prepare the C header file in GIMP as follows:
- Load an image in GIMP
- Scale to 320×200 (detach the link between the sizes)
- Threshold or dither to black and white, play to get a nice result
- Export as C header file
- Feed the C header file to this program
- Convert the result, a binary file into a program like my Convert 8 bit hex formats (included with the KIM-1 Simulator) to a papertape format with the start address of the K-1008 (2000-C000)
- Load the papertape into the KIM-1 or KIM-1 Simulator
Also there are examples of C header and binary K-1008 formatted files.
Sources of LoadK1008 commandline
The folder K-1008 load C Header contains the Freepascal source and original JPG files.
Use the Apple 1 monitor (Wozmon)
Load in Settings the Apple 1 monitor (wozmon) into the free space of the KIM-1 tape ROM.
Start at $1AA0, back to KIM-1 monitor with ‘X’ command.
Changelog
- V 0.9 October 2021 First public beta
- V 0.9.1 November 2021 Fixed key 0 bug (Thanks Liu!)
- V 0.9.2 November 2021 Scrollbars in Load/Save dialog boxes added, Linux tests
- V 0.9.3 November 2021 Added CC65 format symboltable load, added search in symbol table, fixed label display error in disassembly
- V 0.9.4 December 2021 emulated getch in kimsinrom.asm now returns with Y=$FF
- V 0.10.0 January 2022 Added 10 breakpoints and 10 watch points in debugger
- V 0.10.1 January 2022 Save memory bug solved
- V 0.10.2 January 2022 Watchpoints on registers and Stackpointer added
- V 0.11.0 January 2022 Profiler (count how much an opcode is executed) added, Windows main menu to get fast to one of the forms
- V 0.12.0 February 2022 Console cursor control (not finished yet)
- V 0.13.0 February 2022 Main screen updated, more help entries. Console updates (on screen menu for colors) and KIM-1 tape load and save emulation
- V 0.13.1 February 2022 Tested on Ubuntu, small updates and bugs fixed
- V 0.13.2 February 2022 Settings for work directory, KIM tape load/save added to Save/Load memory
- V1.0 February 2022, all planned functionally implemented (the console is now ANSI color enabled)
- V1.0.0.1 February 2022, NumLock numeric keypad added, request for keyboard layout tests: testkeydown program added
- V1.1.1 March 2022 KIMDLE works: free running timer at $1704 and KIM keyboard fixes (no key returns $15)
- V1.1.2 March 2022 Settings for keyboard layout (US International and German for now), key handling KIM keypad and keyboard/console improved, free running timer
- V1.1.4 April 2022 Improved design, use of debugger Run buttions stops main Run/Stop run state
- V1.1.5 August 2022 Save to Define Byte file added, Belgium(french) keyboard layout (tnx Pascal Duquenoy )
- V1.1.6 September 2022 Suppress echo on console like the KIM-1, Focal V3D supported
- V1.1.7 15 November 2022 Tape load/save checksum overflow fixed
- V1.1.8 25 january 2023 Windows 11 keypad shows white image when key pressed, now nothing seen when pressed.
V1.2x retracted
- V1.2.0 30 april 2023 MTU K-1008 Visible Memory implemented
- V1.2.1 19 may 2023 Raspberry Pi added again, compile options optimization high, no debugging
- V1.2.2 30 may 2023 Cleanup all targets and docs (except macOS), Example programs like MS Basic added
- V1.2.3 6 June 2023 Stricter RAM boundaries in Read memory. MacOS version included, thanks Michael Doornbos
- V1.2.4 25 June 2023 Auto scroll bars added for larger forms like debugger. profiler
- V 1.3.0 August 2023, V1.1.8 and changes from V1.2.4 merged
- Auto scroll bars added to larger forms
- Example programs added
- Save and load to file formats bugfixes
- Convert 8 bit Hex format program included in release
- SST switch on keypad shows debugger window
- MTU K-1008 Visible Memory implemented with example programs
- V1.3.1 K-1008 video display updated with File load, Tape load and debugger Refresh button
- V1.3.2 K-1008 images can be loaded from C header files images with GIMP, straight or dithered
- V1.3.3 K-1008 images can be shown in normal window or stretched to correct aspect ratio
- V1.3.4 August 31 Read text file to console improved, improved K-1008 settings
- V1.3.5 October 2 2023 Read text file to console for UNIX and DOS line endings.
Search in Memory, Fill memory and Move/copy memory added to Debugger menu - V1.3.6 October 10 Added Commodore PRG formatted files (binary, starts with load address low byte, high byte
- V1.3.7 Debugged and tested the VT100 codes in the console
- V1.3.8 November 2023 Console now only shows ASCII code 32-126, to get Tiny Basic working.
- V1.3.9 December 2023 TIM format, all forms show in taskbar Windows, bug fixes, file types shown in load, setup with logo
- V 1.4.0 February 2024 Console escape sequence handling improved, more robust, added documentation on color setting, wozmon loaded in Settings
Screenshot of 1.3.3 with ‘correct’ aspect ratio.