On the pagetable Commodore source archive I found the source of the AIM 65 Assembler ROM R3224.
Now on the AIM 65 software page:
Assembler ROM R3224 source from pagetable github
About small SBC systems
On the pagetable Commodore source archive I found the source of the AIM 65 Assembler ROM R3224.
Now on the AIM 65 software page:
Assembler ROM R3224 source from pagetable github
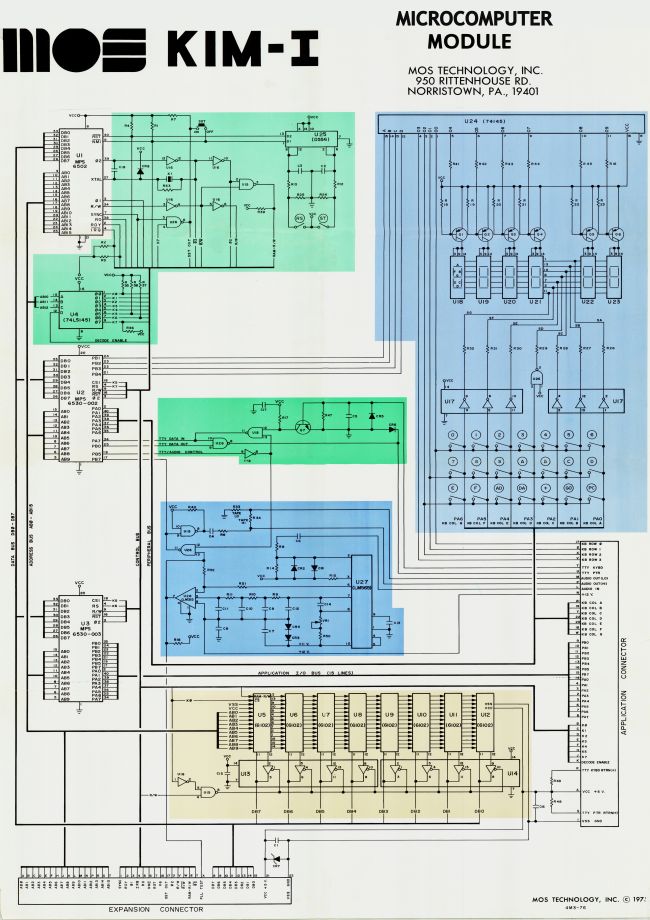
The 6530-002 (the KIM monitor), 6530-003 (the KIM tape routines) and 6530-004 (TIM, the teletype monitor) are in the ROM of these IC’s. Developed in/for/by MOS Technology.
For TIM the Story of TIM (DEMON as Ray Holt called it) tells about Manny Lomas.
It would be nice to know more who did hardware and software design for the KIM-1 (must have been a small team since they are so intertwined) of these innovative early 6502 development.
The story should start with Chuck Peddle and his team. They developed the 6502 and supporting IC’s like 6530 (RRIOT) and 6532 (RIOT).
The story of KIM talks about Don McLaughlin, MOS Technology founder and engineering manager of the project. Peddle and a programming manager named Bob Winterhalt agreed with the idea and the three men began the design. According to MOS Technology employee Al Charpentier, John May did the actual design.
Armin added to his blog page on the Data Handler a Rev Manual with his permission reproduced here.


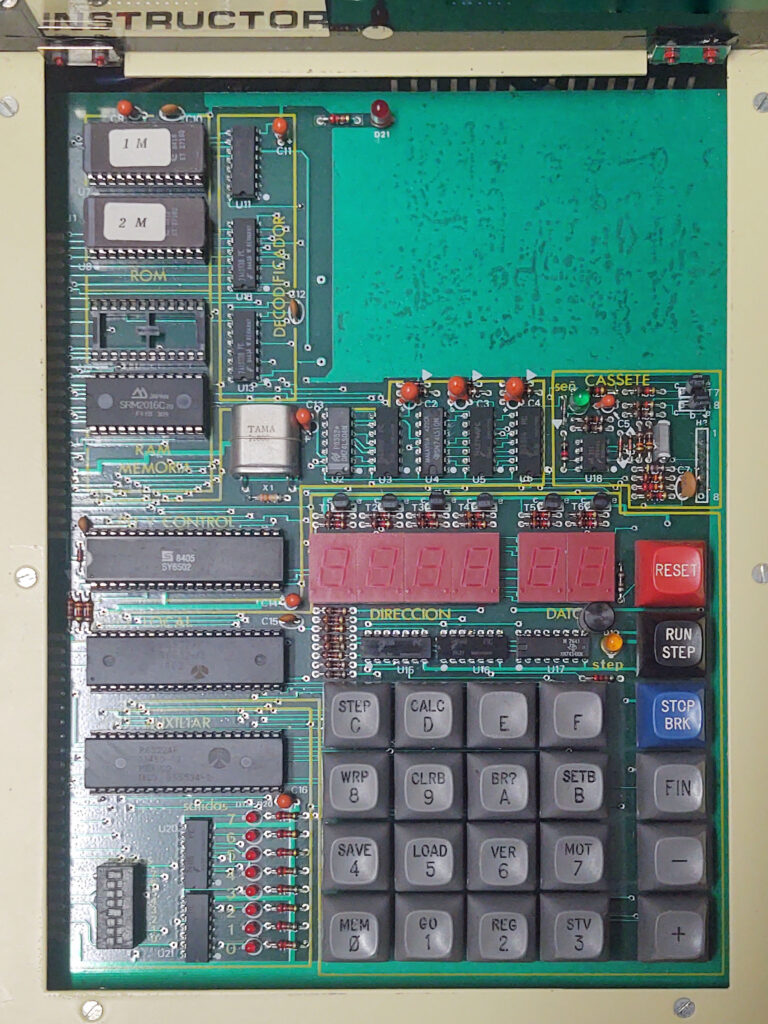
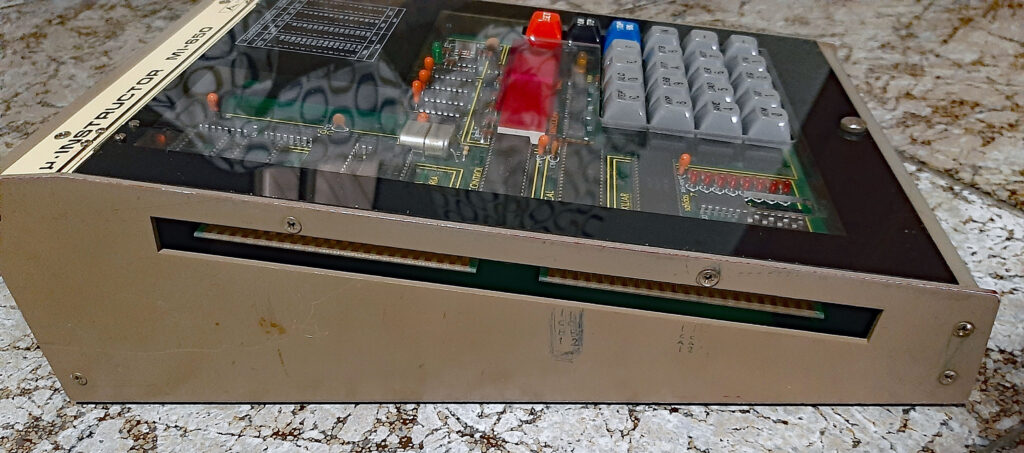
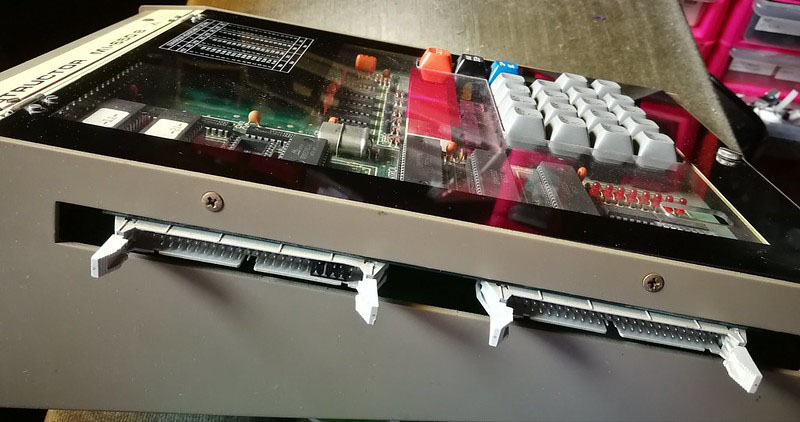
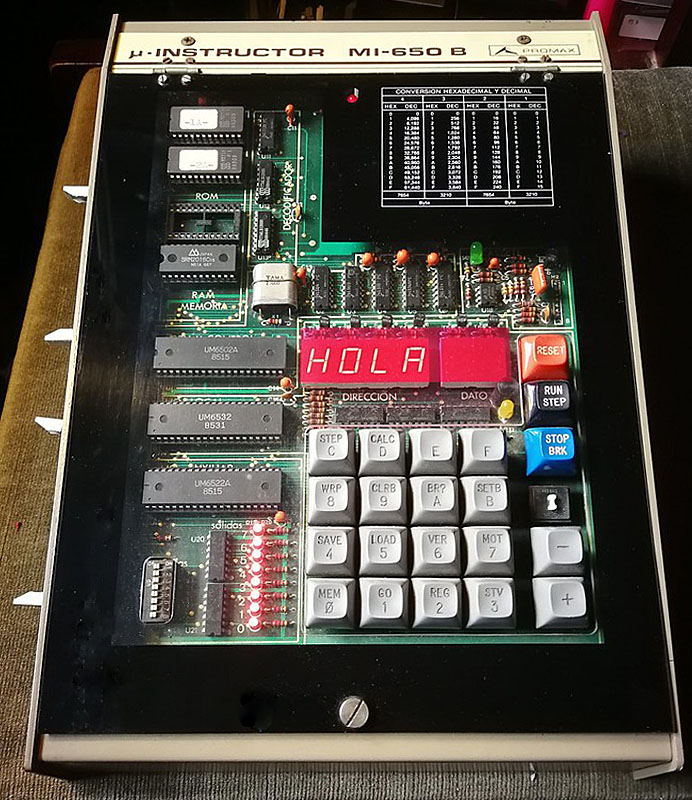
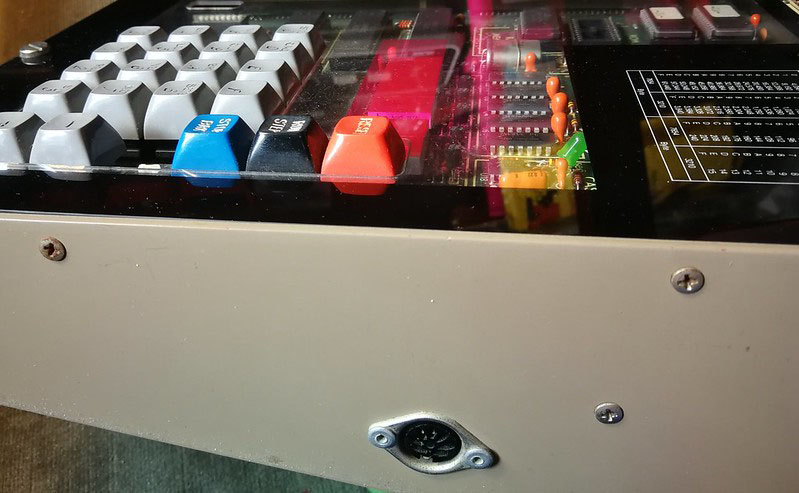
A Spanish firm developed a 6502 trainer, an SBC inspired by the KIM-1. Hexadecimal keyboard, 6 LED displays, I/O to experiment with. Assembled system, boxed, high quality components like mechanical keys. Aimed at education.
On this page:
All three share the same monitor program, patched for the MI-650C to use the 6522.
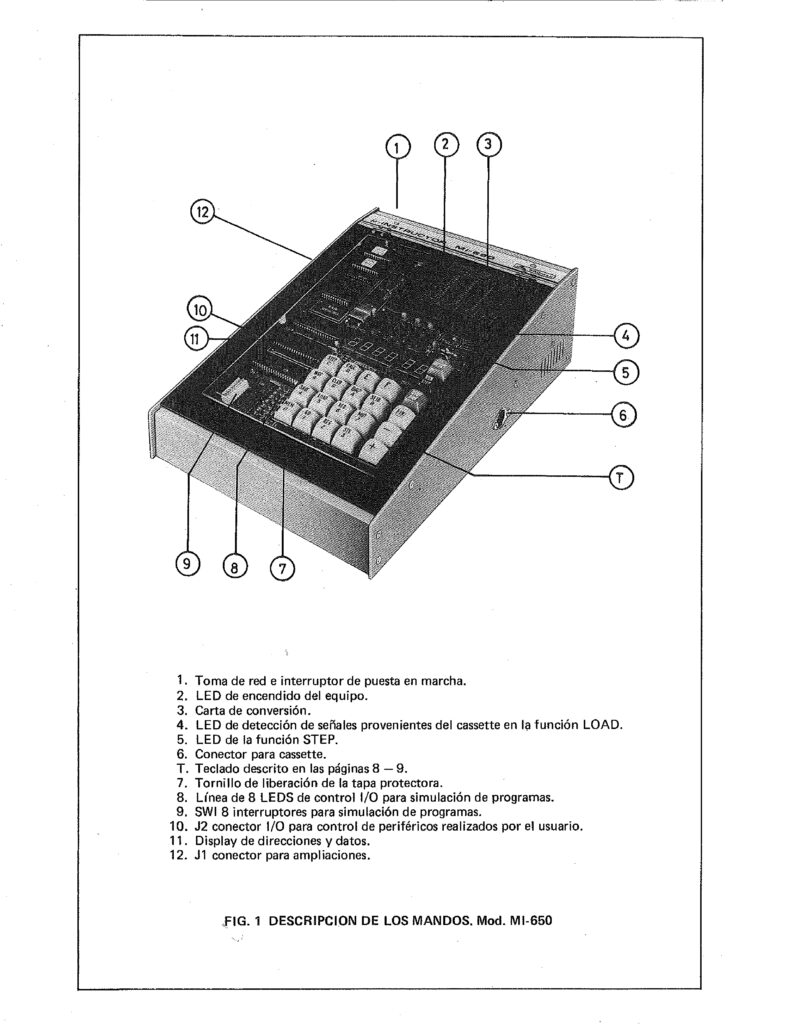
Statement by Promax about the 1979 Educational trainers
Educational instruments division was the result of our close commercial relationships with universities and technical schools. Work here was closely tied to the study plans of universities and technical schools in order to provide the educational material required by a variety of disciplines. Design work was begun on the MI-650B Microprocessor Trainer, based on the 6502 which appeared in 1975.
Updates from various sources, motivated by the find of Jose Vicente Marques Vidal of four MI-650s and our attempt to make them operational again (missing EPROMS mostly).
 |
PROMAX MI 650 μ-instructor |

|
PROMAX MI-650-C Microinstructor (contains ROM listing and more) |
 |
Microprocesadores de 8 bits 6502 promax MI-650C microinstructor |
EPROM images are supplied by John Evans (in the KIM-1 Facebook group) and Youtube user @eeep73 and Dominic Bumbaca.
Identical dumps from two different MI-650s, so good dumps!
Archive with Promax MI-650 EPROM images (2x 2716 EPROMs).
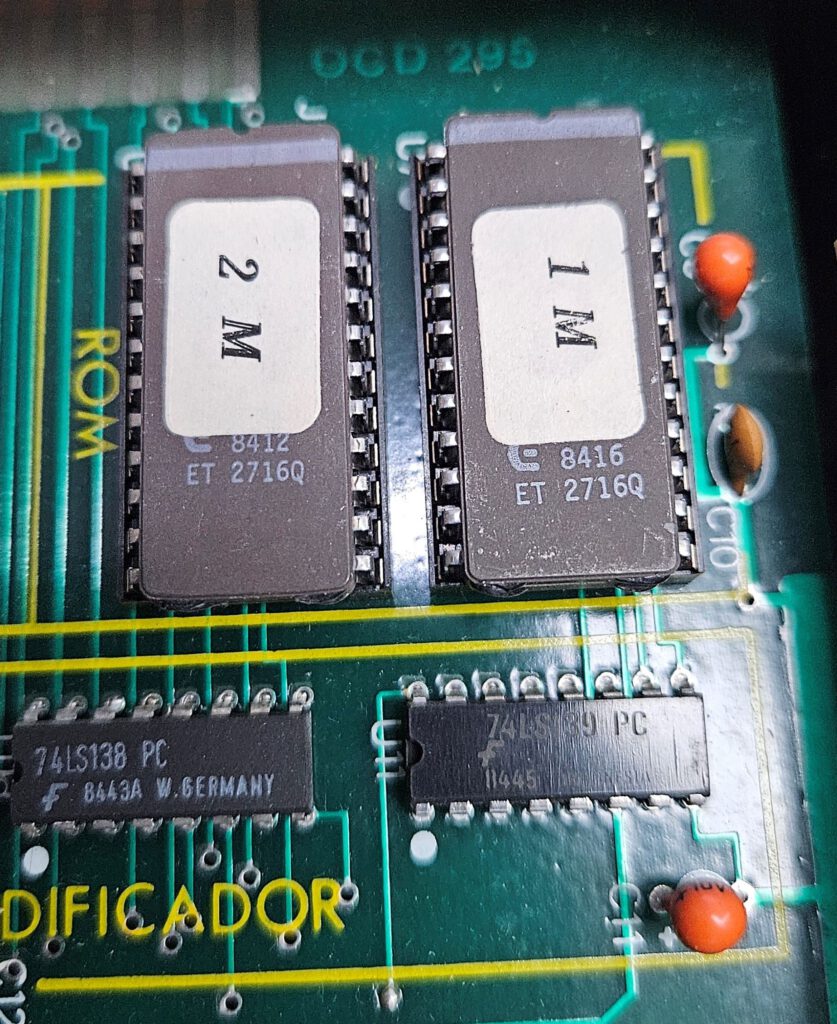

Photo by Dominic Bumbaca
Archive with Promax MI-650 monitor source
Archive with Promax MI-650C monitor source
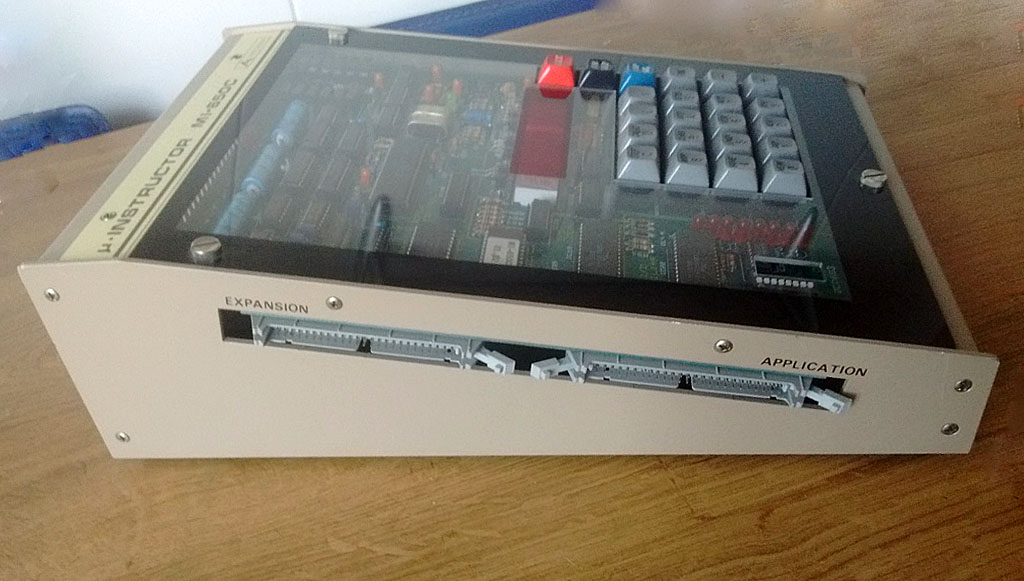
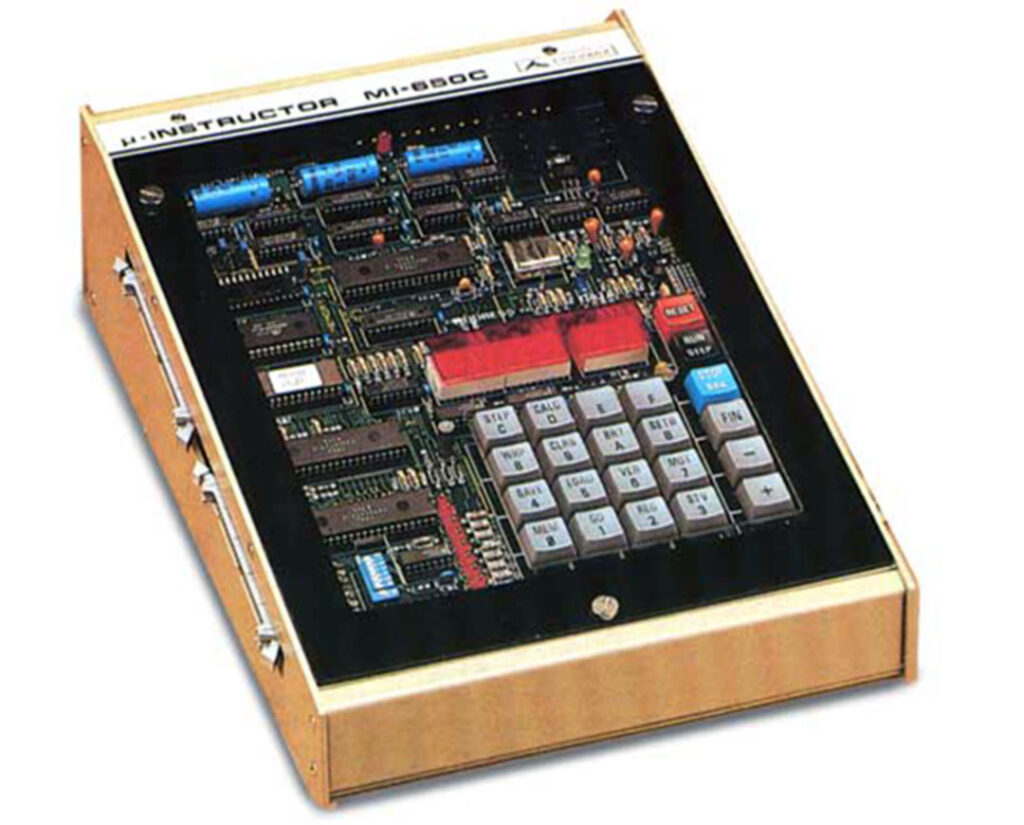
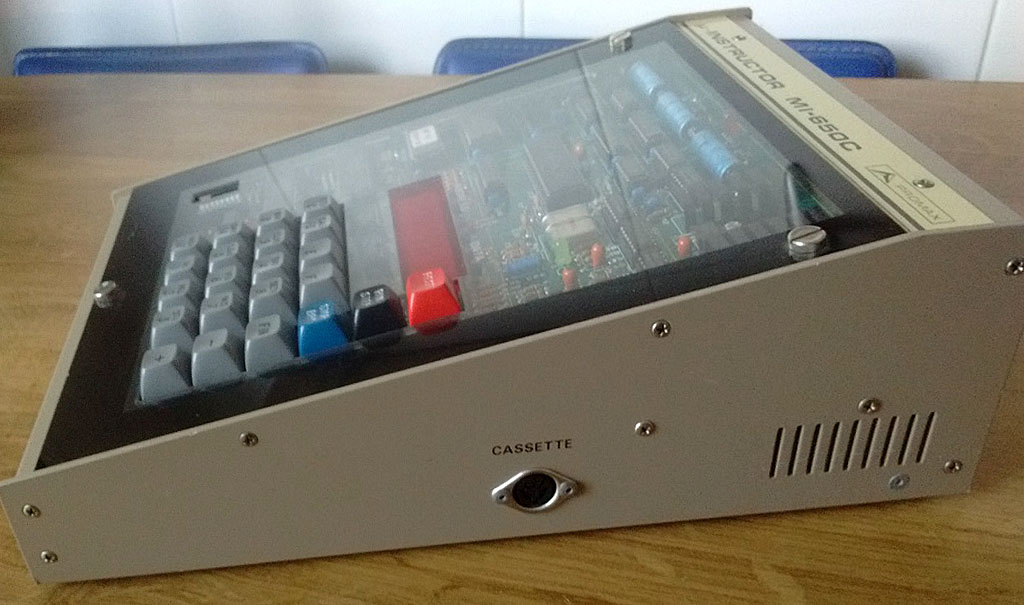



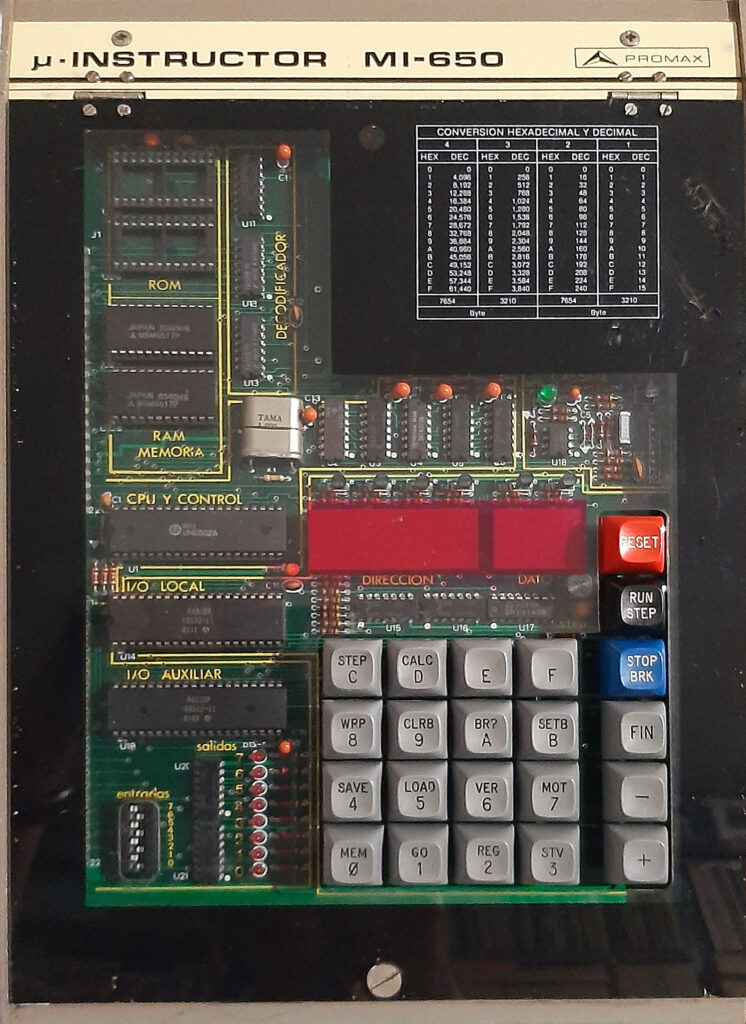










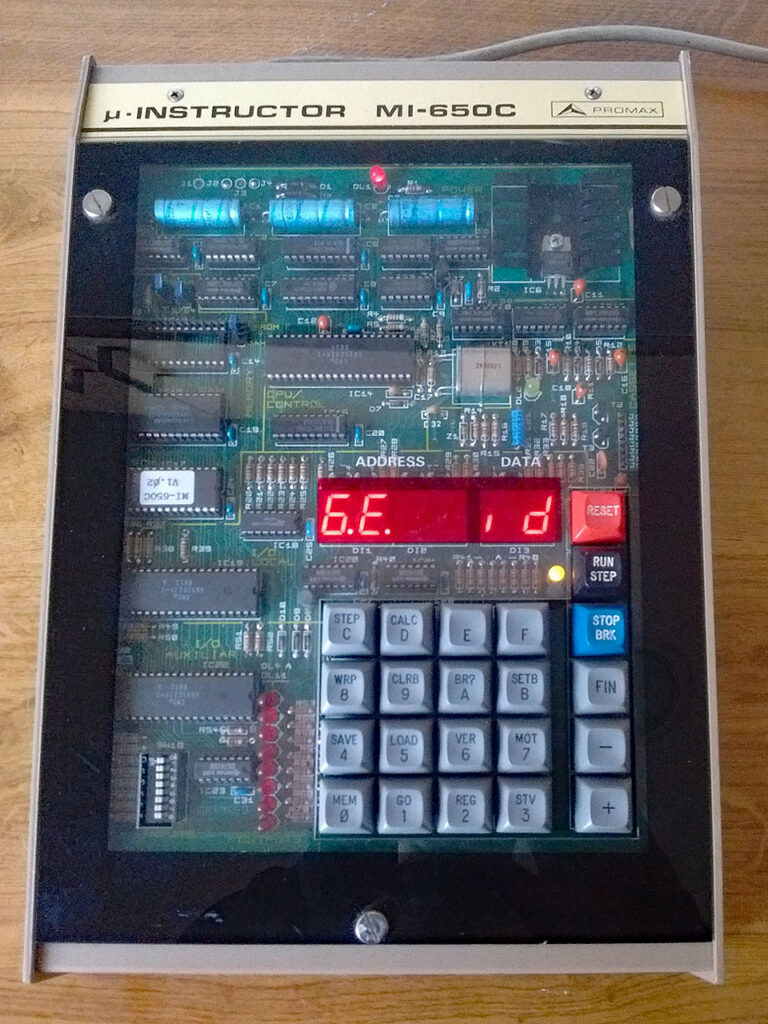


Videos of MI-650 demonstrations
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PypHSDdsIX
Joshy, Forum64 member, cleaned up the high resolution poster. Available here.
Partial scan of The Best of Micro 3: AIM 65 SYM-1 KIM-1 part and General (6522).
With the help of users on the German Classic Computing forum I have added many manuals and magazines in German about those systems:
– AIM 65 PC100 manuals
– MICROMAG magazines
– KIM-1 manuals in German
I also added books on the 6502 in general and on the KIM-1, SYM-1 and AIM 65 to the Books section.
Reading old magazines is always fun, from the period 1976 to 198x magazines were filled with articles on the 6502, the KIM-1 and other SBC’s.
German, Dutch and English magazine articles extracted here.
Kilobaud, Byte, Dr Dobbs and of course the dedicated 6502 User Notes, MICRO Journal and Compute are valuable sources, but look at the many magazines on this page!








 |
A Note on 6502 Indirect Addresssing |
 |
Thoughts on Small Systems and Monitors SYM-1 |
 |
ZX65 Simulating a Micro |

 |
Analysis of the Use of the 6502’s Opcodes |

 |
Interfacing the 68000 to an AIM 65 |
 |
Improvement upon a Division Program by Leventhal |
 |
6502_hacks |
 |
ACTxx_Cross Assemblers |
 |
Decoding Efficiency and Speed Pros and Cons of Table Loo-up |
 |
Saving And Restoring Registers |
 |
SBC TSX TXS Instructions 6800 6502 |
 |
Use of NOP Codes as Labels |