I2C Bus interface
Hardware
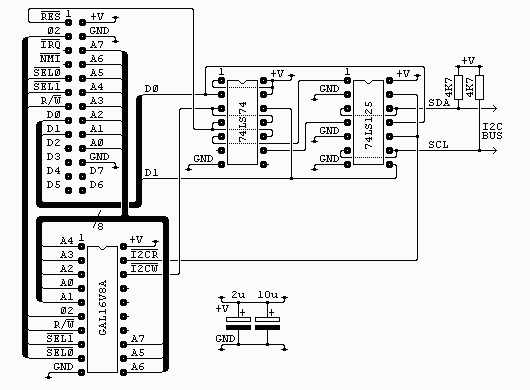
The connector on the top left of the diagram is from my own 6502 boards (see the sbc project) and is as it is for two reasons. It’s easy to wire on a stripboard layout and I have a lot of 26 way ribbon, headers and plugs. All the signals are directly from the 6502 except /SEL0 and /SEL1 which are used to select the block $F1xx with /SEL0 = 1 and /SEL1 = 0.
There is no socket shown for the I2C bus, this is up to the user.The two capacitors are low ESR electrolytics and are placed near the GAL and between the two chips. If you don’t have this type to hand you can use standard electrolytics with some low value ceramic capacitor, say 0.1uF, in parallel.
The GAL16V8A is used purely to generate the read and write strobes. Each is a negative going pulse coincident with phase 2. The interface uses just one byte in the address range. For anyone interested the equations for this chip are in i2c_01.pld and can be compiled with WinCUPL. The fuse file, i2c_01.jed and the compiler list file i2c_01.txt are also included.
The 74LS74 is used to latch the two lowest bits of the data bus during write access to the interface. The reset line is connected so that both of these outputs are set at startup (this disables the I2C bus until required). This is very similar to my AT keyboard with the exeption that reset sets the opposite state.
The outputs from the latches are used to drive the enable pins on two of the four buffers from the 74LS125, these are then used to drive the data and clock lines of the I2C bus. The buffers have their inputs tied low so behave like open collector outputs when used like this. The other two buffers are used to drive the data bus during read access.
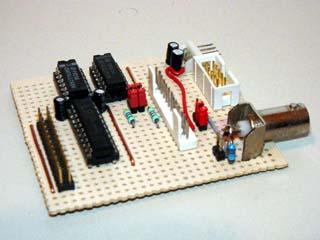
The finished board
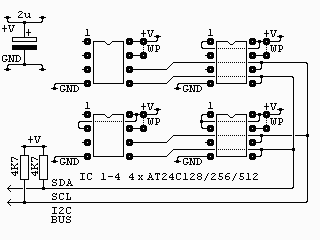
256k byte memory
Software
The software has a four main routines to handle the I2C bus
| SendAddr | Send start and slave address to the I2C bus. |
| SendData | Send data byte(s) to an addressed device. |
| ReadData | Read data byte(s) from an addressed device. |
| StopI2c | generates a stop condition on the i2c bus. |
This is a description of all the I2C routines
SendAddr
This routine sends the slave address to the I2C bus. There are a number of locations that need set-up before this routine is called. Each device has an 8 bit address, the lowest bit of which is a read/write bit, this address is set in I2cAddr. Next is the byte count, if you are just addressing the device this can be zero but otherwise it is the byte pair in I2cCountL/H. Lastly, if there is data to be sent, is the buffer pointer TxBuffL/H. This should be set to the start of the data to be sent. If all is well this routine exits with Cb=0 and the bus in an held state, you can then either send data, receive data or just send stop.
ReadData
This routine reads I2cCountL/H bytes from an already addressed device. It should be entered with RxBuffL/H pointing to a suitable buffer area. On exit Cb=0 if there were no errors and the I2C bus is in a held state, you can then either receive more data or just send stop.
SendData
The same as ReadData but sends I2cCountL/H bytes to an already addressed device. Again on exit Cb=0 if there were no errors and the I2C bus is in a held state, you can then either send more data or just send stop.
StopI2c
This routine just generates a stop condition on i2c bus. On entry it is assumed only that the clock is held low.
ByteIn
Read a byte from the I2C bus, the byte is returned in A. Entry to this routine should be with the bus in a held state and it exits with the bus in the same state. Note there is no timeout on this routine so it could end up waiting for ever. After this routine you should send an ack but if it’s the end of what you want you can just send stop.
ByteOut
Send a byte to the I2C bus, the byte to be sent is in A. Entry to this routine should be with the bus in a held state and it exits with the bus in the same state. Note there is no timeout on this routine so it could end up waiting for ever. Returns with the ack bit in Cb=0.
DoAck
Send ack bit, the ack bit state to send is in Cb. Entry is with the clock low, then ack needs to be set and then the clock released. The routine then waits for the clock to rise before pulling it low and then exiting.
GetAck
Get the ack bit, the received ack bit is returned in Cb. Entry is with the clock low, then the data line is released followed by the clock. Then, once the clock rises, the ack bit is read.
View the I2C driver assembler source
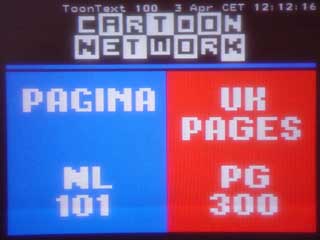
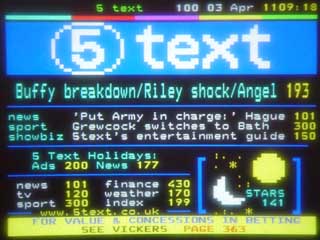
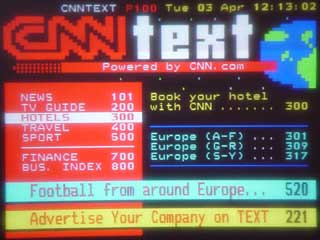
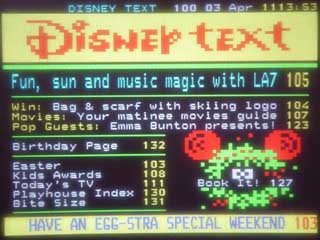
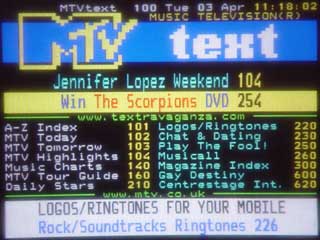
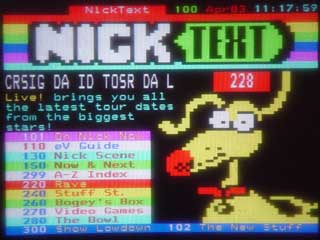
EHBASIC teletext driver. This is a simple page select driver for the SAA5243 + SAA5231 teletext chipset
The board in use and screen shots

;------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ ; ; The following is 6502 code for an I2C driver. It acts only as master. ; ; I2C uses two bi-directional (OC) lines: clock and data. The maximum bit rate for ; slow mode is 100kbits/sec (fast mode is not supported) but with a 1.8MHz 6502 the ; best you will get is about 43kbits/sec. As the 6502, which is the master, controls ; the clock line, the processor speed should not be a problem. ; ; To work as a slave the 6502 would need extra hardware to detect the start condition, ; the stop condition and extra code to handle collisions. ; This is saved for a later project. ; ; Devices are accessed using the following four subroutines. ; ; SendAddr ; This routine sends the slave address to the I2C bus. It can also send any ; required register address bytes by setting them up as you would data to be sent. ; No stop is sent so you can either read or write after calling this routine. ; SendData ; Send data byte(s) to an addressed device. Set the count in I2cCountL/H and ; point to the data with TxBuffL/H. No stop is sent after calling this routine. ; ReadData ; Read data byte(s) from an addressed device. Set the count in I2cCountL/H and ; point to the buffer with RxBuffL/H. No stop is sent after calling this routine. ; StopI2c ; generates a stop condition on the i2c bus ; ; Each device has an 8 bit address, the lowest bit of which is a read/write bit. ; ;------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ I2CPort = $F121 ; i2c bus port, o.c. outputs, tristate inputs ; bit 0 is data [SDA] ; bit 1 is clock [SLC] ; bits 2 to 7 are unused RxBuffL = $F1 ; receive buffer pointer low byte TxBuffL = RxBuffL ; the same (can't do both at once!) RxBuffH = $F2 ; receive buffer pointer high byte TxBuffH = RxBuffH ; the same (can't do both at once!) ByteBuff = $F3 ; byte buffer for Tx/Rx routines I2cAddr = $F4 ; Tx/Rx address I2cCountL = $F5 ; Tx/Rx byte count low byte I2cCountH = $F6 ; Tx/Rx byte count high byte ;------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ *= $2000 JMP SendData ; vector to send data JMP ReadData ; vector to read data JMP SendAddr ; vector to send slave address JMP StopI2c ; vector to send stop ;------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ ; ; send the slave address for an i2c device. if I2cCountL is non zero then that number ; of bytes will be sent after the address (to allow register addressing, required on ; some devices). RxBuff is a pointer, in page zero, to the transmit buffer exits with ; the clock low and Cb=0 if all ok routine entered with the i2c bus in a stopped state ; [SDA=SCL=1] SendAddr LDA I2CPort ; get i2c port state ORA #$01 ; release data STA I2CPort ; out to i2c port LDA #$03 ; release clock STA I2CPort ; out to i2c port LDA #$01 ; set for data test WaitAD BIT I2CPort ; test the clock line BEQ WaitAD ; wait for the data to rise LDA #$02 ; set for clock test WaitAC BIT I2CPort ; test the clock line BEQ WaitAC ; wait for the clock to rise JSR StartI2c ; generate start condition LDA I2cAddr ; get address (including read/write bit) JSR ByteOut ; send address byte BCS StopI2c ; branch if no ack LDA I2cCountL ; get byte count BNE SendData ; go send if not zero RTS ; else exit ;------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ ; ; send data to an already addressed i2c device. I2cCountL/H is the number of bytes to ; send RxBuff is a pointer, in page zero, to the transmit buffer exits with Cb=0 if ; all ok. it is assumed at least one byte is to be sent routine entered with the i2c ; bus in a held state [SCL=0] SendData INC I2cCountH ; increment count high byte LDY #$00 ; set index to zero WriteLoop LDA (RxBuffL),Y ; get byte from buffer JSR ByteOut ; send byte to device BCS StopI2c ; branch if no ack INY ; increment index BNE NoHiWrInc ; branch if no rollover INC RxBuffH ; else increment pointer high byte NoHiWrInc DEC I2cCountL ; decrement count low byte BNE WriteLoop ; loop if not all done DEC I2cCountH ; increment count high byte BNE WriteLoop ; loop if not all done RET ;------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ ; ; get data from already addressed i2c device. I2cCountL/H is the number of bytes to ; get, RxBuff is a pointer, in page zero, to the receive buffer. exits with Cb = 0 if ; all ok it is assumed at least one byte is to be received. the routine is entered ; with the i2c bus in a held state [SCL=0] ReadData LDY #$00 ; set index to zero ReadLoop DEC I2cCountL ; decrement count low byte JSR ByteIn ; get byte from device LDA I2cCountL ; get count low byte CMP #$01 ; compare with end count + 1 LDA I2cCountH ; get count high byte SBC #$00 ; subtract carry, leaves Cb = 0 for last byte JSR DoAck ; send ack bit LDA ByteBuff ; get byte from byte buffer STA (TxBuffL),Y ; save in device buffer INY ; increment index BNE NoHiRdInc ; branch if no rollover INC TxBuffH ; else increment pointer high byte NoHiRdInc LDA I2cCountL ; get count low byte BNE ReadLoop ; loop if not all done DEC I2cCountH ; decrement count high byte LDA I2cCountH ; get count high byte CMP #$FF ; compare with end count BNE ReadLoop ; loop if not all done RTS ;------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ ; ; generate stop condition on i2c bus. it is assumed only that the clock is low on ; entry to this routine. StopI2c LDA #$00 ; now hold the data down STA I2CPort ; out to i2c port ; NOP ; need this if running > 1.9MHz LDA #$02 ; release the clock STA I2CPort ; out to i2c port ; NOP ; need this if running > 1.9MHz LDA #$03 ; now release the data (stop) STA I2CPort ; out to i2c port RTS ;------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ ; ; generate start condition on i2c bus. it is assumed that both clock and data are ; high on entry to this routine. note, another condition is A = $02 on entry StartI2c STA I2CPort ; out to i2c port ; NOP ; need this if running > 1.9MHz LDA #$00 ; clock low, data low STA I2CPort ; out to i2c port RTS ;------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ ; ; output byte to 12c bus, byte is in A. returns Cb = 0 if ok. clock should be low ; after generating a start or a previously sent byte ; exits with clock held low ByteOut STA ByteBuff ; save byte for transmit LDX #$08 ; 8 bits to do OutLoop LDA #$00 ; unshifted clock low ROL ByteBuff ; bit into carry ROL A ; get data from carry STA I2CPort ; out to i2c port ; NOP ; need this if running > 1.9MHz ORA #$02 ; clock line high STA I2CPort ; out to i2c port LDA #$02 ; set for clock test WaitT1 BIT I2CPort ; test the clock line BEQ WaitT1 ; wait for the clock to rise LDA I2CPort ; get data bit AND #$01 ; set clock low STA I2CPort ; out to i2c port DEX ; decrement count BNE OutLoop ; branch if not all done ;------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ ; ; clock is low, data needs to be released, then the clock needs to be released then ; we need to wait for the clock to rise and get the ack bit. GetAck LDA #$01 ; float data STA I2CPort ; out to i2c port LDA #$03 ; float clock, float data STA I2CPort ; out to i2c port LDA #$02 ; set for clock test WaitGA BIT I2CPort ; test the clock line BEQ WaitGA ; wait for the clock to rise LDA I2CPort ; get data LSR A ; data bit to Cb LDA #$01 ; clock low, data released STA I2CPort ; out to i2c port RTS ;------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ ; ; input byte from 12c bus, byte is returned in A. entry should be with the clock low ; after generating a start or a previously sent byte ; exits with clock held low ByteIn LDX #$08 ; 8 bits to do LDA #$01 ; release data STA I2CPort ; out to i2c port InLoop LDA #$03 ; release clock STA I2CPort ; out to i2c port LDA #$02 ; set for clock test WaitR1 BIT I2CPort ; test the clock line BEQ WaitR1 ; wait for the clock to rise LDA I2CPort ; get data ROR A ; bit into carry ROL ByteBuff ; bit into buffer LDA #$01 ; set clock low STA I2CPort ; out to i2c port DEX ; decrement count BNE InLoop ; branch if not all done RTS ;------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ ; ; clock is low, ack needs to be set then the clock released then we wait for the ; clock to rise before pulling it low and finishing. Ack bit is in Cb DoAck LDA #$00 ; unshifted clock low ROL A ; get ack from carry STA I2CPort ; out to i2c port ; NOP ; need this if running > 1.9MHz ORA #$02 ; release clock STA I2CPort ; out to i2c port LDA #$02 ; set for clock test WaitTA BIT I2CPort ; test the clock line BEQ WaitTA ; wait for the clock to rise LDA I2CPort ; get ack back AND #$01 ; hold clock STA I2CPort ; out to i2c port RTS ;------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ END
EhBASIC Teletext page viewer
This is a simple page select driver for the SAA5243 + SAA5231 teletext chipset. X is valid as a wildcard digit.
1 REM set memory size to 8192 for this program 5 REM simple teletext decoder page driver 6 REM there is no page read, output is via 7 REM teletext chip video out 10 REM set I2C interface values 20 TT = 34 : REM teletext chip 12c address 30 SB = $2000 : REM send byte 40 RB = £2003 : REM read byte (not used) 50 CL = $F5 : REM # bytes low (i2ccountL) 60 BL = $F1 : REM buffer ptr low (rxbuffl) 70 AD = $F4 : REM device address (i2caddr) 80 BF = $4000 : REM buffer address 90 DIM TR(10) : REM register buffer 110 GOSUB 800 : REM setup chip 120 TR(8) = 0 : REM no clear display 130 TR(9) = 0 : REM set row 140 TR(10) = 0 : REM set column 150 GOSUB 838 : REM set registers 8 to 10 160 P3 = 49 : REM 1 161 P2 = 48 : REM 0 162 P1 = 48 : REM 0 170 GOSUB 370 : REM set search page 200 REM main program loop 210 DO 220 GOSUB 300 : REM select page 230 LOOP 299 END : REM never gets here 300 REM Select page 310 INPUT "Page no.";P$ 320 IF LEN(P$)<>3 THEN 310 330 P$ = UCASE$(P$) : REM "x" to "X" 340 P1=ASC(RIGHT$(P$,1)) : REM 1s character ASCII value 350 P2=ASC(MID$(P$,2,1)) : REM 10s character ASCII value 360 P3=ASC(LEFT$(P$,1)) : REM 100s character ASCII value 365 REM dispaly the searched for page number 370 POKE BF,8 : REM register address 380 POKE BF+1,0 : REM set x value 390 POKE BF+3,0 : REM set y value 400 POKE BF+3,2 : REM set white 410 POKE BF+4,P3 : REM display page 100s 420 POKE BF+5,P2 : REM display page 10s 430 POKE BF+6,P1 : REM display page 1s 440 POKE AD,TT : REM set device address 450 DOKE BL,BF : REM set the buffer address 460 DOKE CL,7 : REM seven bytes to send 470 CALL SB : REM send byte(s) 475 REM set the page to search for 480 P1=P1-32 : REM calsulate page 1s (ASCII - 48 + 16) 490 P2=P2-32 : REM calculate page 10s (ASCII - 48 + 16) 500 P3=P3-24 : REM calculate page 100s (ASCII - 48 + 24) 510 IF P1=56 THEN P1 = 0 : REM allow wildcard "X" 520 IF P2=56 THEN P2 = 0 : REM allow wildcard "X" 530 IF P3=64 THEN P3 = 8 : REM allow wildcard "X" 540 POKE BF,2 : REM register address 550 POKE BF+1,0 560 POKE BF+2,P3 570 POKE BF+3,P2 580 POKE BF+4,P1 590 POKE AD,TT : REM set device address 600 DOKE BL,BF : REM set the buffer address 610 DOKE CL,5 : REM five bytes to send 620 CALL SB : REM send byte(s) 630 RETURN 799 END 800 REM setup teletext registers 801 RESTORE 910 802 FOR X = 1 TO 5 804 READ TR(X) 806 POKE BF+X,TR(X) 808 NEXT 810 POKE BF,1 : REM register address 812 POKE AD,TT : REM set device address 814 DOKE BL,BF : REM set the buffer address 816 DOKE CL,6 : REM six bytes to send 818 CALL SB : REM send byte 819 RESTORE 935 820 FOR X = 4 TO 7 822 READ TR(X) 824 POKE BF-3+X,TR(X) 826 NEXT 828 POKE BF,4 : REM register address 830 POKE AD,TT : REM set device address 832 DOKE BL,BF : REM set the buffer address 834 DOKE CL,5 : REM five bytes to send 836 CALL SB : REM send byte 838 RESTORE 980 839 FOR X = 8 TO 10 840 READ TR(X) 842 POKE BF-7+X,TR(X) 844 NEXT 846 POKE BF,8 : REM register address 848 POKE AD,TT : REM set device address 850 DOKE BL,BF : REM set the buffer address 852 DOKE CL,4 : REM four bytes to send 854 CALL SB : REM send byte 856 RETURN 900 REM default values for registers 1 - 3 910 DATA 4 920 DATA 0 930 DATA 25,16,16 935 REM default values for registers 4 - 7 940 DATA 0 950 DATA 207 960 DATA 0 970 DATA 39 975 REM default values for registers 8 - 10 980 DATA 16 985 DATA 0 990 DATA 0 [code] <a name="i2c_jed"></a> <b>GAL logic fuse file</B> [code] CUPL(WM) 4.7b Serial# XX-xxxxxxxx Device g16v8as Library DLIB-h-36-2 Created Fri Mar 23 10:30:16 2001 Name I2C_01 Partno 00 Revision 01 Date 19/03/01 Designer Lee Company Assembly None Location *QP20 *QF2194 *G0 *F0 *L00000 10101011011110110111011010010110 *L00256 10101011011110110111101010010110 *L02048 00000000001100000011000000100000 *L02112 00000000001111111111111111111111 *L02144 11111111111111111111111111111111 *L02176 111111111111111110 *C0E15 *77C0
Name I2C_01 ; PartNo 00 ; Date 19/03/01 ; Revision 01 ; Designer Lee ; Company ; Assembly None ; Location ; Device g16v8as ; /* This GAL is the select logic for the I2C interface board */ /* Logic minimisations None */ /* Optimisations None */ /* Download JEDEC/POF/PRG */ /* Doc File Options fuse plot, equations */ /* Output None */ /* *************** INPUT PINS *********************/ PIN 1 = A4 ; /* address bus */ PIN 2 = A3 ; /* address bus */ PIN 3 = A2 ; /* address bus */ PIN 4 = A0 ; /* address bus */ PIN 5 = A1 ; /* address bus */ PIN 6 = p02 ; /* CPU phase 2 */ PIN 7 = RW ; /* read write */ PIN 8 = !SEL1 ; /* block select */ PIN 9 = !SEL0 ; /* block select */ PIN 11 = A6 ; /* address bus */ PIN 12 = A5 ; /* address bus */ PIN 13 = A7 ; /* address bus */ /* *************** OUTPUT PINS *********************/ PIN 19 = !I2CR ; /* I2C port read strobe */ PIN 18 = !I2CW ; /* I2C port write strobe */ /*PIN 17 = ; /* */ /*PIN 16 = ; /* */ /*PIN 15 = ; /* */ /*PIN 14 = ; /* */ /* intermediate terms */ ADDR = !A7 & !A6 & A5 & !A4 & !A3 & !A2 & !A1 & A0 & !SEL0 & SEL1 ; /* F121h (0010 0001) /* Output terms */ I2CR = ADDR & RW & p02 ; /* I2C port read strobe */ I2CW = ADDR & !RW & p02 ; /* I2C port write strobe */
*******************************************************************************
I2C_01
*******************************************************************************
CUPL(WM) 4.7b Serial# XX-xxxxxxxx
Device g16v8as Library DLIB-h-36-2
Created Fri Mar 23 10:30:16 2001
Name I2C_01
Partno 00
Revision 01
Date 19/03/01
Designer Lee
Company
Assembly None
Location
===============================================================================
Expanded Product Terms
===============================================================================
ADDR =>
A0 & !A1 & !A2 & !A3 & !A4 & A5 & !A6 & !A7 & !SEL0 & SEL1
KBR =>
A0 & !A1 & !A2 & !A3 & !A4 & A5 & !A6 & !A7 & RW & !SEL0 & SEL1 & p02
KBW =>
A0 & !A1 & !A2 & !A3 & !A4 & A5 & !A6 & !A7 & !RW & !SEL0 & SEL1 & p02
===============================================================================
Symbol Table
===============================================================================
Pin Variable Pterms Max Min
Pol Name Ext Pin Type Used Pterms Level
--- -------- --- --- ---- ------ ------ -----
A0 4 V - - -
A1 5 V - - -
A2 3 V - - -
A3 2 V - - -
A4 1 V - - -
A5 12 V - - -
A6 11 V - - -
A7 13 V - - -
ADDR 0 I 1 - -
! KBR 19 V 1 8 1
! KBW 18 V 1 8 1
RW 7 V - - -
! SEL0 9 V - - -
! SEL1 8 V - - -
p02 6 V - - -
LEGEND D : default variable F : field G : group
I : intermediate variable N : node M : extended node
U : undefined V : variable X : extended variable
T : function
===============================================================================
Fuse Plot
===============================================================================
Syn 02192 - Ac0 02193 x
Pin #19 02048 Pol x 02120 Ac1 x
00000 -x-x-x--x----x--x---x--x-xx-x--x
00032 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
00064 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
00096 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
00128 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
00160 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
00192 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
00224 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Pin #18 02049 Pol x 02121 Ac1 x
00256 -x-x-x--x----x--x----x-x-xx-x--x
00288 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
00320 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
00352 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
00384 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
00416 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
00448 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
00480 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Pin #17 02050 Pol x 02122 Ac1 -
00512 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
00544 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
00576 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
00608 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
00640 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
00672 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
00704 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
00736 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Pin #16 02051 Pol x 02123 Ac1 -
00768 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
00800 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
00832 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
00864 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
00896 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
00928 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
00960 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
00992 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Pin #15 02052 Pol x 02124 Ac1 -
01024 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
01056 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
01088 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
01120 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
01152 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
01184 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
01216 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
01248 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Pin #14 02053 Pol x 02125 Ac1 -
01280 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
01312 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
01344 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
01376 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
01408 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
01440 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
01472 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
01504 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Pin #13 02054 Pol x 02126 Ac1 -
01536 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
01568 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
01600 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
01632 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
01664 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
01696 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
01728 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
01760 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Pin #12 02055 Pol x 02127 Ac1 -
01792 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
01824 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
01856 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
01888 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
01920 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
01952 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
01984 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
02016 xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
LEGEND X : fuse not blown
- : fuse blown
===============================================================================
Chip Diagram
===============================================================================
______________
| I2C_01 |
A4 x---|1 20|---x Vcc
A3 x---|2 19|---x !KBR
A2 x---|3 18|---x !KBW
A0 x---|4 17|---x
A1 x---|5 16|---x
p02 x---|6 15|---x
RW x---|7 14|---x
!SEL1 x---|8 13|---x A7
!SEL0 x---|9 12|---x A5
GND x---|10 11|---x A6
|______________|