By Bob Applegate
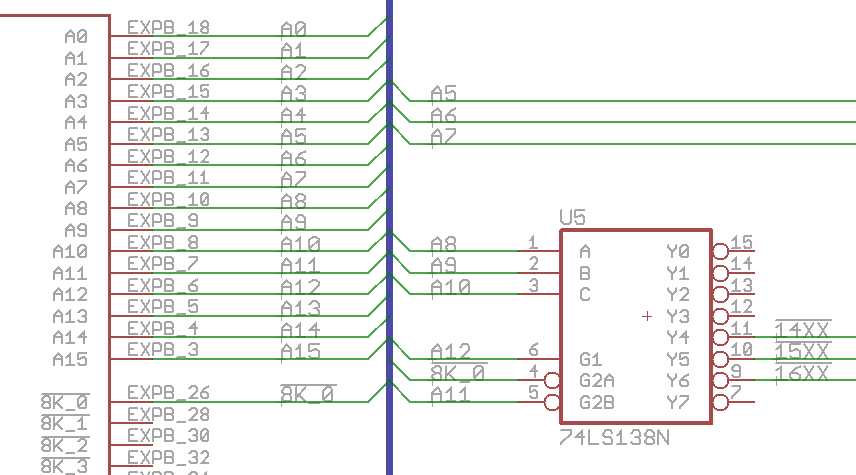
Adding I/O devices that don’t need much address space. On the KIM-1, the space from 1400-17FF is grouped into the K0 block but only 17xx are used, leaving 1400-16FF open for use. To decode that range into four blocks of 256 bytes is easy using a single chip and a few signals from the KIM Clone expansion bus:
Everyone has a 74LS138 in their parts collection, so just connect a few signals from the expansion bus and use one of the three signals from the 138 to decode which block you want to use. Use the A0-A7 address lines to decode into smaller pieces.
See also:
MACH-9 MMS Inc 6809 CPU Plug-in for AIM 65
Royce Taft has a MACH-9 MMS Inc 6809 CPU Plug-in for AIM 65 and reverse engineered it.
He sent me his design to be pu...
PicoSYM, a SYM-1 emulator on a Raspberry Pico
Emulation of a Synertek Sym-1 on a Raspberry Pi Pico 1 (W).
By andysa on the emulation forum on 6502.org
Here is t...
Amazing it works!
After publishing the photos of the transistors used in the KIM-1 a discussion started on forum64.de in the 'Instandsetzu...
Transistors in the KIM-1
Even a microprocessor based computer as the KIM-1 required some simple transistors.
To drive the LEDs some extra curren...